

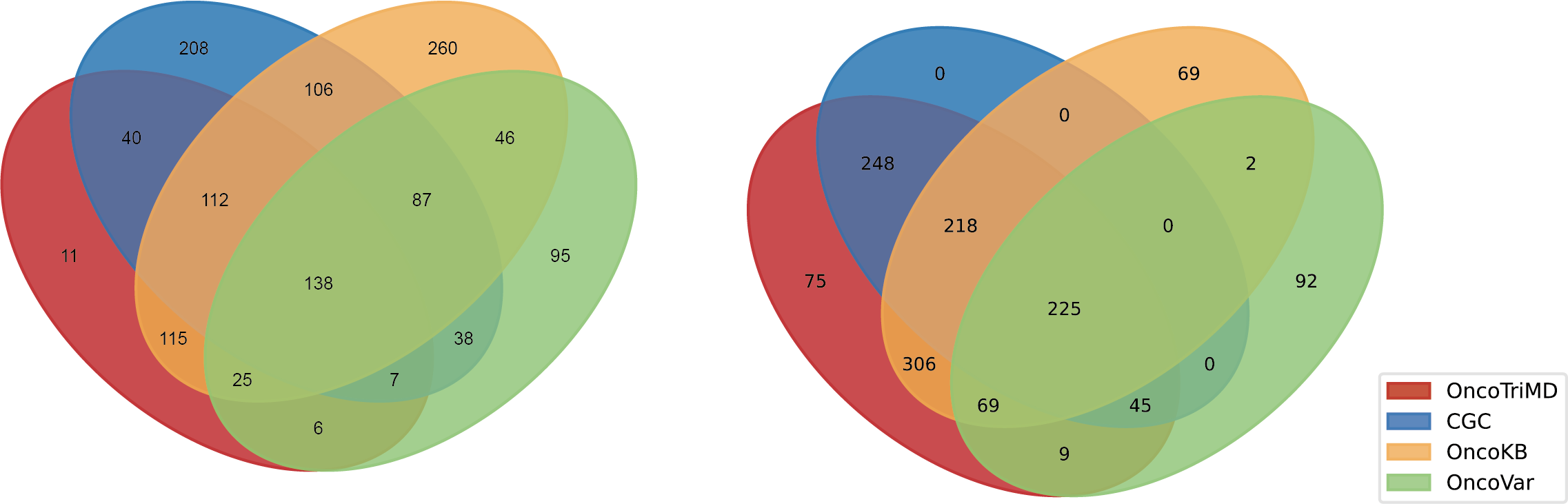
Left: the overlap for OncoTriMD-defined Level 1A genes; Right: the overlap for OncoTriMD-defined Level 1 genes, encompassing both Level 1A and Level 1B.
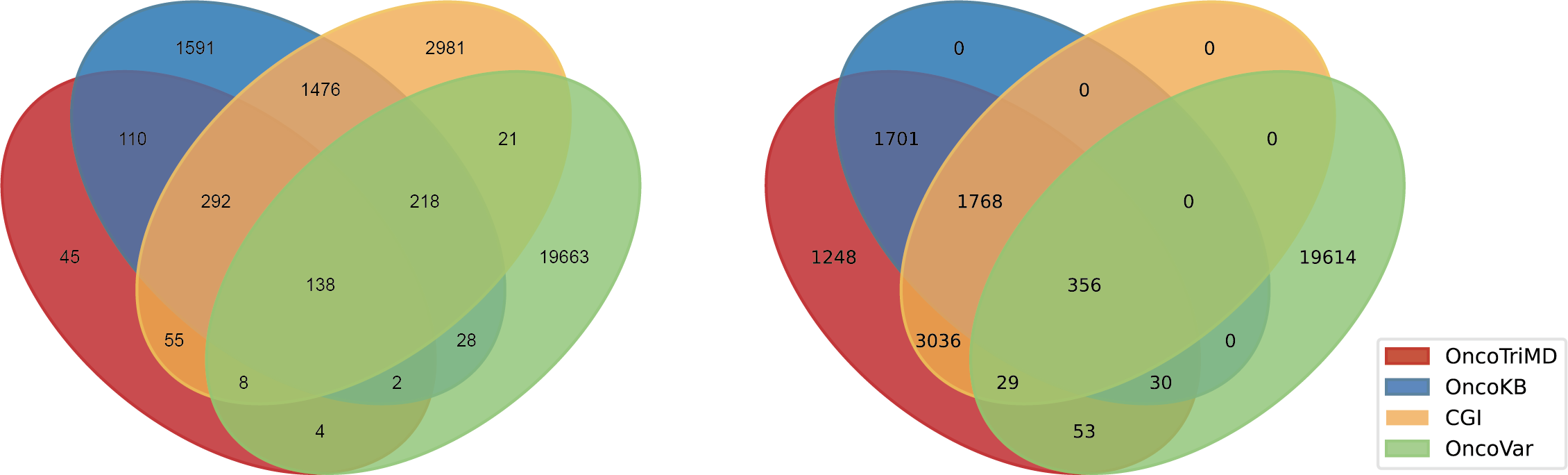
Left: the overlap for OncoTriMD-defined Level 1A mutations; Right: the overlap for OncoTriMD-defined Level 1 mutations, encompassing both Level 1A and Level 1B.
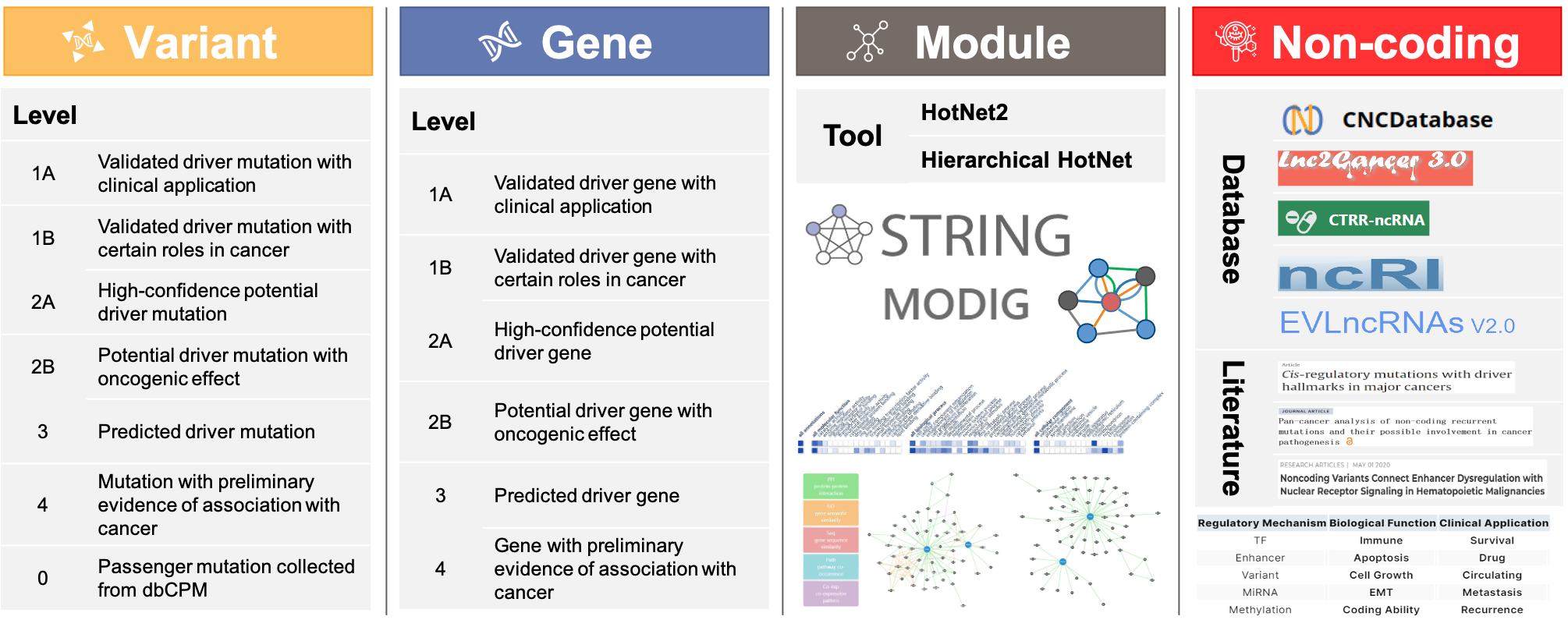
The following tables summarize the data sources collected by this database and their brief descriptions, including external databases, PubMed literature, prediction algorithms, etc.
| Abbreviation | Cancer type | Tissue type | Abbreviation | Cancer type | Tissue type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | Acute Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow |
| LAML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | ACC | Adrenocortical Carcinoma | Adrenal cortex |
| B-ALL | B Cell Acute Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | BPLL | B-cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow |
| LIAD | Benign Liver Tumour | Liver | BTCA | Biliary Tract Carcinomas | Biliary tract |
| BLCA | Bladder Cancer | Bladder | BOCA | Bone Cancer | Bones |
| LGG | Brain Lower Grade Glioma | Brain | BRCA | Breast Invasive Carcinoma | Breast |
| CESC | Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Cervix | CHOL | Cholangiocarcinoma | Bile ducts |
| CLLE | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | CLL | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow |
| CMDI | Chronic Myeloid Disorders | Blood and bone marrow | CML | Chronic Myeloid Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow |
| COAD | Colon Adenocarcinoma | Colon | COADREAD | Colon and Rectal Cancer | Colon and rectum |
| COCA | Colorectal Cancer | Colon and rectum | EOPC | Early Onset Prostate Cancer | Prostate |
| ETMR | Embryonal Carcinoma | Germ cells | ESAD | Esophageal Adenocarcinoma | Esophagus |
| ESCA | Esophageal Carcinoma | Esophagus | GACA | Gastric Cancer | Stomach |
| GBM | Glioblastoma Multiforme | Brain | HNSC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Head and neck |
| HGG | High Grade Glioma | Brain | KICH | Kidney Chromophobe | Kidney |
| KIRC | Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma | Kidney | KIRP | Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma | Kidney |
| LICA | Liver Cancer | Liver | LINC | Liver Cancer - NCC | Liver |
| LIRI | Liver Cancer - RIKEN | Liver | LIHC | Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Liver |
| LIHM | Liver Hepatocellular Macronodules | Liver | LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma | Lung |
| LUSC | Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Lung | DLBC | Lymphoid Neoplasm Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma | Lymph nodes |
| MALY | Malignant Lymphoma | Lymph nodes | MB | Medulloblastoma | Brain |
| MELA | Melanoma | Skin | MESO | Mesothelioma | Mesothelial tissue (lining of organs) |
| NACA | Nasopharyngeal Cancer | Nasopharynx | NKTL | Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma | Lymph nodes |
| NBL | Neuroblastoma | Nerve tissue | NSCLC | Non Small Cell Lung Cancer | Lung |
| ORCA | Oral Cancer | Oral cavity | OV | Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma | Ovary |
| PANCAN | PanCancer | Various tissues | PAAD | Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | Pancreas |
| PACA | Pancreatic Cancer | Pancreas | PAEN | Pancreatic Cancer Endocrine neoplasms | Pancreas |
| PBCA | Pediatric Brain Cancer | Brain | PEME | Pediatric Medulloblastoma | Brain |
| PCPG | Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma | Adrenal gland | PA | Pilocytic Astrocytoma | Brain |
| PRAD | Prostate Adenocarcinoma | Prostate | READ | Rectum Adenocarcinoma | Rectum |
| RECA | Renal Cancer | Kidney | RT | Rhabdoid Tumors | Various tissues (primarily affects children) |
| SARC | Sarcoma | Connective tissues (e.g., bone, muscle, cartilage) | SKCA | Skin Adenocarcinoma | Skin |
| SKCM | Skin Cutaneous Melanoma | Skin | LMS | Soft Tissue Cancer - Leiomyosarcoma | Soft tissues (e.g., smooth muscle) |
| STAD | Stomach Adenocarcinoma | Stomach | T-ALL | T Cell Acute Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow |
| TGCT | Testicular Germ Cell Tumor | Testicles | THYM | Thymoma | Thymus |
| THCA | Thyroid Carcinoma | Thyroid gland | UTCA | Uterine Cancer - Carcinosarcoma | Uterus |
| UCS | Uterine Carcinosarcoma | Uterus | UCEC | Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma | Uterus (endometrium) |
| UVM | Uveal Melanoma | Eye (uveal tract) | WT | Wilms Tumor | Kidney |
| Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor | Jaw (odontogenic tissue) | Ameloblastoma | Jaw (odontogenic tissue) | ||
| Aneurysm | Blood vessels | Angiosarcoma | Blood vessels or lymphatic vessels | ||
| Basal Cell Carcinoma | Skin | Brain Cancer | Brain | ||
| Cardiac Cancer | Heart | Chondrosarcoma | Cartilage | ||
| Chordoma | Spine or skull base | Choriocarcinoma | Placenta | ||
| Cutaneous Squamous Carcinoma | Skin | Ductal Carcinomas | Ducts | ||
| Epithelial Cancer | Epithelial tissues | Ewing Sarcoma | Bone or soft tissues | ||
| External Auditory Canal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Ear canal | Fibroma | Fibrous tissues | ||
| Gallbladder Cancer | Gallbladder | Gastrointestinal Cancer | Digestive system | ||
| Germ Cell Tumor | Reproductive organs | Glioma | Brain or spinal cord | ||
| Hemangioma | Blood vessels | Hematologic Cancer | Blood or bone marrow | ||
| Invasive Mucinous Adenocarcinoma | Various tissues | Kaposi's Sarcoma | Blood vessels or lymphatic vessels | ||
| Laryngeal and Hypopharyngeal Carcinoma | Larynx or hypopharynx | Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | ||
| Lung Cancer | Lung | Lymphoblastic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | ||
| Lymphoma | Lymph nodes or lymphatic tissues | Malignant Mesothelioma | Mesothelial tissues (lining of organs) | ||
| Maxillary Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Maxillary sinus | Meningioma | Meninges | ||
| Monocytic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | Murine Plasmacytomas | Plasma cells | ||
| Myeloid Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | Myeloma | Bone marrow | ||
| Neural System Tumors Syndrome | Nervous system | Neurofibromatosis | Nervous system | ||
| Neurological Tumors | Nervous system | Oligoastrocytoma | Brain | ||
| Oligodendroglioma | Brain | Osteosarcoma | Bone | ||
| Parathyroid Cancer | Parathyroid glands | Parotid Cancer | Parotid glands | ||
| Penile Cancer | Penile | Phaeochromocytoma | Adrenal glands | ||
| Pituitary Tumor | Pituitary gland | Prolactinoma | Pituitary gland (prolactin-secreting cells) | ||
| Promyelocytic Leukemia | Blood and bone marrow | Retinoblastoma | Retina | ||
| Retroperitoneal Liposarcoma | Retroperitoneal tissues | Salivary Gland Cancer | Salivary glands | ||
| Seminoma | Testicles | Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Sinonasal cavity | ||
| Small Cell Lung Cancer | Lung | Spinal Cancer | Spinal cord | ||
| Squamous Carcinoma | Squamous epithelial cells | Synovial Sarcoma | Soft tissues around joints (synovial tissues) | ||
| Teratocarcinoma | Germ cells (ovaries or testicles) | Testicular Cancer | Testicles | ||
| Tongue Cancer | Tongue | Transitional Cell Carcinoma | Urinary tract | ||
| Trophoblastic Tumor | Placenta | Urothelial Cancer | Urinary tract | ||
| Uterus Cancer | Uterus | Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Vulva | ||
| Wilms' tumor | Kidney |
| Data Type | Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer genomics | TCGA(The Cancer Genome Atlas) MC3 | |
| ICGC(International Cancer Genome Consortium) Release28 | ||
| METABRIC(Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium) | ||
| Driver mutation resource | dbNSFP v4.3a | dbNSFP is a database developed for functional prediction and annotation of all potential non-synonymous single-nucleotide variants (nsSNVs) in the human genome. |
| CanDriS | CanDriS is a software which uses an empirical Bayesian procedure to calculate the posterior probability of a site to be cancer-driving for all sites in a gene. | |
| FASMIC | FASMIC is a comprehensive database containing experimental evidence on the functional impacts of somatic mutations detected in human cancer. | |
| COSMIC | COSMIC, the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer, is the world's largest and most comprehensive resource for exploring the impact of somatic mutations in human cancer. | |
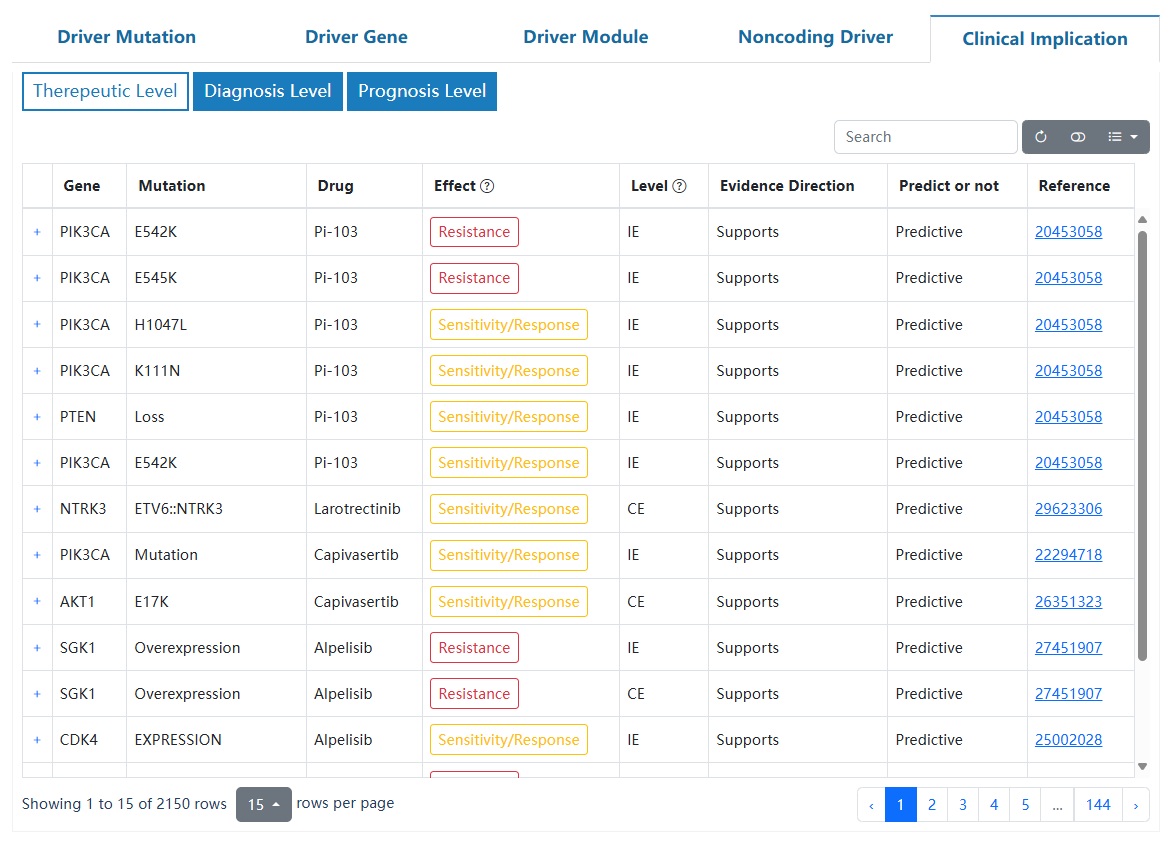
| Clinical implication info | CGI | Cancer Genome Interpreter is a database that helps interpret the results of cancer genomic testing and provides information on the clinical relevance of genetic variants in cancer |
| PMKB | Precision Medicine Knowledge Base (PMKB) is an interactive online application for collaborative editing, maintenance, and sharing of structured clinical-grade cancer mutation interpretations. | |
| OncoKB | OncoKB™ annotates the biologic and oncogenic effects and prognostic and predictive significance of somatic molecular alterations. Potential treatment implications are stratified by the level of evidence that a specific molecular alteration is predictive of drug response on the basis of US Food and Drug Administration labeling, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, disease-focused expert group recommendations, and scientific literature. | |
| CLinVar | ClinVar is a freely accessible, public archive of reports of the relationships among human variations and phenotypes, with supporting evidence. | |
| CIViC | CIViC provides an educational resource to support better understanding of the current state of precision medicine. It may also provide useful summaries and links to relevant published evidence for the clinical relevance of specific variants. |
| Data Type | Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sequences and Annotations of Human Genes | Ensembl GRCh37 Release75 | Ensembl GRCh75 is a database that provides a comprehensive and integrated source of annotation of mainly vertebrate genome sequences. |
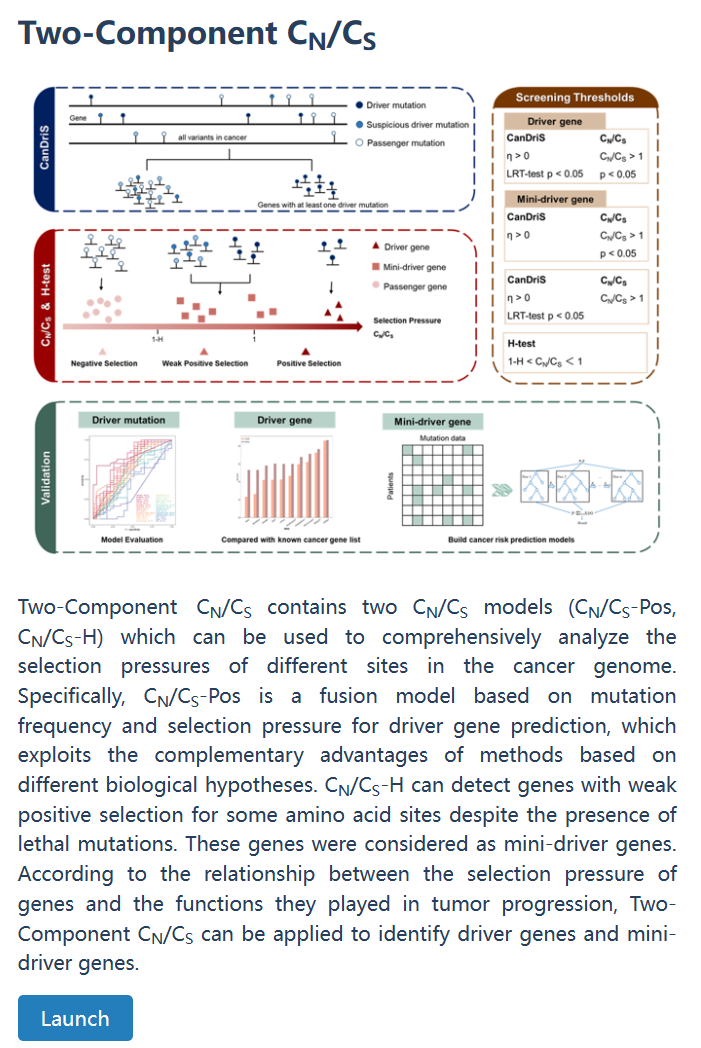
| Driver gene resource | Two-Component CN/CS | Two-component CN/CS contains two CN/CS models (CN/CS-Pos, CN/CS-H) which can be used to comprehensively analyze the selection pressures of different sites in the cancer genome. According to the relationship between the selection pressure of genes and the functions they played in tumor progression, Two-component CN/CS can be applied to identify driver genes and mini-driver genes. |
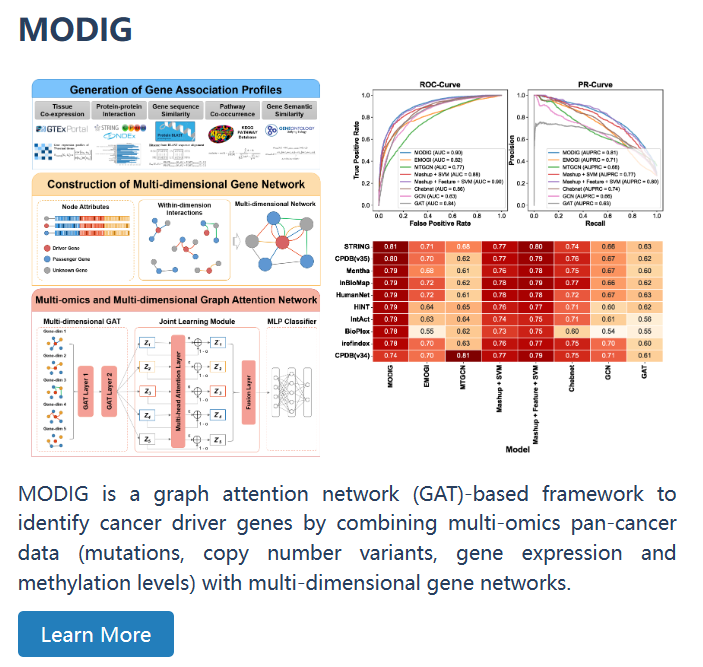
| MODIG | MODIG, a graph attention network (GAT)-based framework to identify cancer driver genes by combining multi-omics pan-cancer data (mutations, copy number variants, gene expression and methylation levels) with multi-dimensional gene networks. | |
| COSMIC CGC | The Cancer Gene Census (CGC) is an ongoing effort to catalogue those genes which contain mutations that have been causally implicated in cancer and explain how dysfunction of these genes drives cancer. | |
| SEECancer | SEECancer database aims to present the comprehensive cancer evolutionary stage-specific somatic events (including early-specific, late-specific, relapse-specific, metastasis-specific, drug-resistant and drug-induced genomic events) and their temporal orders. | |
| OncoKB | OncoKB™ annotates the biologic and oncogenic effects and prognostic and predictive significance of somatic molecular alterations. Potential treatment implications are stratified by the level of evidence that a specific molecular alteration is predictive of drug response on the basis of US Food and Drug Administration labeling, National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, disease-focused expert group recommendations, and scientific literature. | |
| CCGD | The Candidate Cancer Gene Database (CCGD) is developed to disseminate the results of transposon-based forward genetic screens in mice that identify candidate cancer genes. | |
| PanSoftware | PanSoftware applied to PanCancer data identified 299 cancer driver genes with implications regarding their anatomical sites and cancer/cell types. | |
| NCG v7.1 | NCG collects 3,347 cancer driver genes from Census of Cancer Genes (CGC), Vogelstein, Science 2013, Saito, Nature 2020 and screenings of cancer tissues, as well as 95 healthy drivers from screenings of non-cancer tissues. | |
| CIViC | CIViC provides an educational resource to support better understanding of the current state of precision medicine. It may also provide useful summaries and links to relevant published evidence for the clinical relevance of specific variants. | |
| CancerMine | CancerMine is a literature-mined database of drivers, oncogenes and tumor suppressors in cancer. It is a valuable resource for cancer researchers and clinicians to understand the genetic underpinnings of different cancer types. | |
| TSGene | TSGene 2.0 aims to support cancer research by maintaining a high quality tumor suppressor gene list for pan-cancer analysis. This database serves a comprehensive, fully classified, richly and accurately annotated tumor suppressor gene knowledgebase, with extensive cross-references and querying interfaces freely accessible to the scientific community. | |
| ONGene | ONGene database aims to support oncogene research by maintaining a high quality oncogene database that serves as a comprehensive, fully classified, richly and accurately annotated oncogene resource, with extensive cross-references and querying interfaces freely accessible to the scientific community. | |
| CIGene | CIGene serves as a valuable resource to efficiently define cancer initiation events, including somatic mutations, gene regulation, and gene interactions. | |
| GCGene | GCGene is a comprehensive gene resource for gastric cancer. It includes: Curated gastric cancer genes from thousands of literatures, comprehensive annotations including regulatory information, gene expression profiles from normal and cancer tissues, somatic mutations from multiple cancer types. | |
| ECGene | ECGene is committed to establishing a comprehensive gene resource for endometrial cancer. It includes: Curated endometrial cancer genes from thousands of literatures, gene expression summary for type 1 and type 2 endometrial cancers from 12 studies, comprehensive annotations such as color marked KEGG pathways, precomputed lncRNA co-expression networks using TCGA matched samples, somatic mutations from thousands cancer patients | |
| MSGene | MSGene, a database that aims to provide an unbiased, centralized, publicly available and regularly updated collection of genetic association studies performed on MS phenotypes. | |
| BCGene | Brain cancer-related genes and their associated literature, as well as quickly determine related brain functions by using pre-computed analyses of cancer genomics and the Allen Brain Atlas. | |
| Driver gene annotation | dbNSFP v4.3a | dbNSFP is a database developed for functional prediction and annotation of all potential non-synonymous single-nucleotide variants (nsSNVs) in the human genome. |
| OGEE | OGEE is an Online GEne Essentiality database to enhance our understanding of the essentiality of genes. | |
| CSGene | CSGene is committed to establishing a comprehnsive gene resource for cell senescence. It includes: Literature data, biological pathways, gene expression profiles, homologs. | |
| CellAge | CellAge Database of Cell Senescence Genes. Cell senescence can be defined as the irreversible cessation of cell division of normally proliferating cells. Human cells become senescent from progressive shortening of telomeres as cells divide, stress or oncogenes. | |
| REGene | REGene is committed to establishing a comprehnsive gene resource for Regeneration. It includes: Literature data, biological pathways,gene expression profiles, orghologs | |
| TissGDB | TissGDB is the tissue-specific gene annotation database in cancer, aiming to provide a resource or reference for cancer and the related disease studies in the context of tissue specificity. |
| Data Type | Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Driver module | HotNet2 | HotNet2 (diffusion-oriented subnetworks) is a general algorithm for identifying high weight subnetworks in a vertex-weighted network. HotNet2 was developed for identifying significantly mutated groups of interacting genes from large cancer sequencing studies. |
| Hierarchical-hotnet | Hierarchical HotNet, an algorithm that finds a hierarchy of altered subnetworks. Hierarchical HotNet assesses the statistical significance of the resulting subnetworks over a range of biological scales and explicitly controls for ascertainment bias in the network. | |
| ActivePathways | ActivePathways, a tool for integrating multiple omics datasets and identifying gene sets that are over-represented in a list or matrix of genes. | |
| Interactome | STRING | STRING is a database of known and predicted protein-protein interactions. The interactions include direct (physical) and indirect (functional) associations; they stem from computational prediction, from knowledge transfer between organisms, and from interactions aggregated from other (primary) databases. |
| MODIG | MODIG, a graph attention network (GAT)-based framework to identify cancer driver genes by combining multi-omics pan-cancer data (mutations, copy number variants, gene expression and methylation levels) with multi-dimensional gene networks. |
| Data Type | Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Database | CNCDatabase | CNCDatabase provides the list of non-coding cancer drivers in gene promoters, enhancers, ncRNAs and CTCF-cohesin insulators published in over 25 studies. |
| Lnc2Cancer v3.0 | Lnc2Cancer is a manually curated database that provides comprehensive experimentally supported associations between lncRNA or circRNA and human cancer. | |
| EVLncRNAs v2.0 | EVlncRNAs is a comprehensive, manually curated, high-quality and freely accessible resource of integrated sequence, structure, functional, and phenotypic information of experimentally validated long noncoding RNAs from all species. | |
| CTRR-ncRNA | CTRR-ncRNA is the first public database that curates experimentally supported data related to non-coding RNAs related to cancer resistance and cancer recurrence from published literature, aiming to provide a comprehensive and precise resource for research on treatment resistance and recurrence prevention. | |
| ncRI | Non-coding RNAs in Inflammation (ncRI) provides a manually curated database for experimentally validated non-coding RNAs in inflammatary disease. | |
| Literature | Noncoding Variants Connect Enhancer Dysregulation with Nuclear Receptor Signaling in Hematopoietic Malignanc | Combining targeted resequencing of hematopoietic lineage-associated CREs and mutation discovery, this study uncovered 1,836 recurrently mutated CREs containing leukemia-associated noncoding variants. By enhanced CRISPR/dCas9-based CRE perturbation screening and functional analyses, this study identified 218 variant-associated oncogenic or tumor-suppressive CREs in human leukemia. |
| Cis-regulatory mutations with driver hallmarks in major cancers | By integrating whole-genome sequencing, genetic data, and allele-specific gene expression from TCGA, this study identified 320 somatic non-coding mutations that affect gene expression in cis (FDR<0.25). | |
| Pan-cancer analysis of non-coding recurrent mutations and their possible involvement in cancer pathogenesis | This study identified 21,574 recurrent mutations in non-coding regions that were shared by at least two different samples from both COSMIC and TCGA databases. Among them, 580 candidate cancer-related non-coding recurrent mutations were identified based on epigenomic and chromatin structure datasets. |
OncoTriMD offers a user-friendly interface to facilitate efficient usage. The 'Home' page allows for a quick search by 'mutation', 'gene', 'module', 'non-coding', and 'cancer type', enabling users to promptly access relevant information.
Additionally, on the search page of each main section, users can conduct more detailed searches based on the filtering criteria provided on each search page.
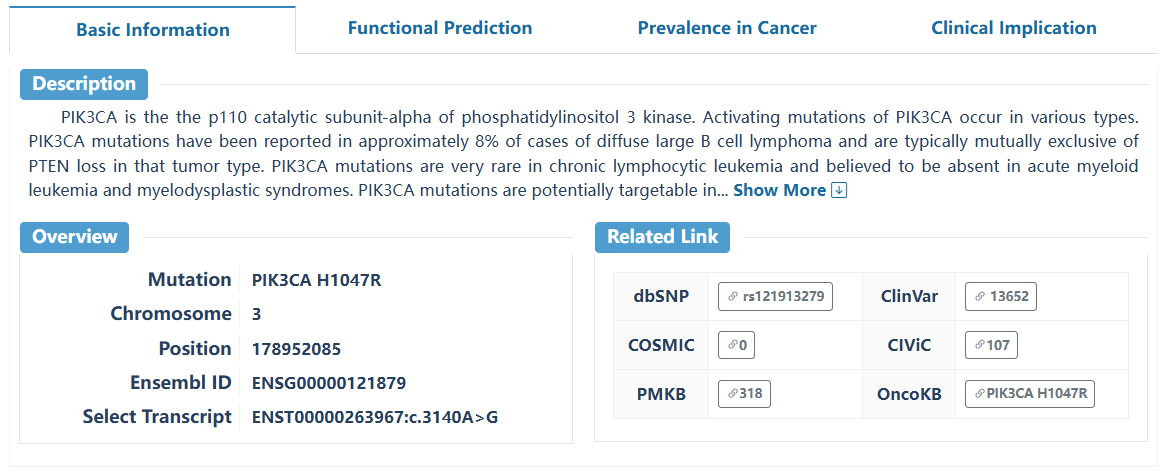
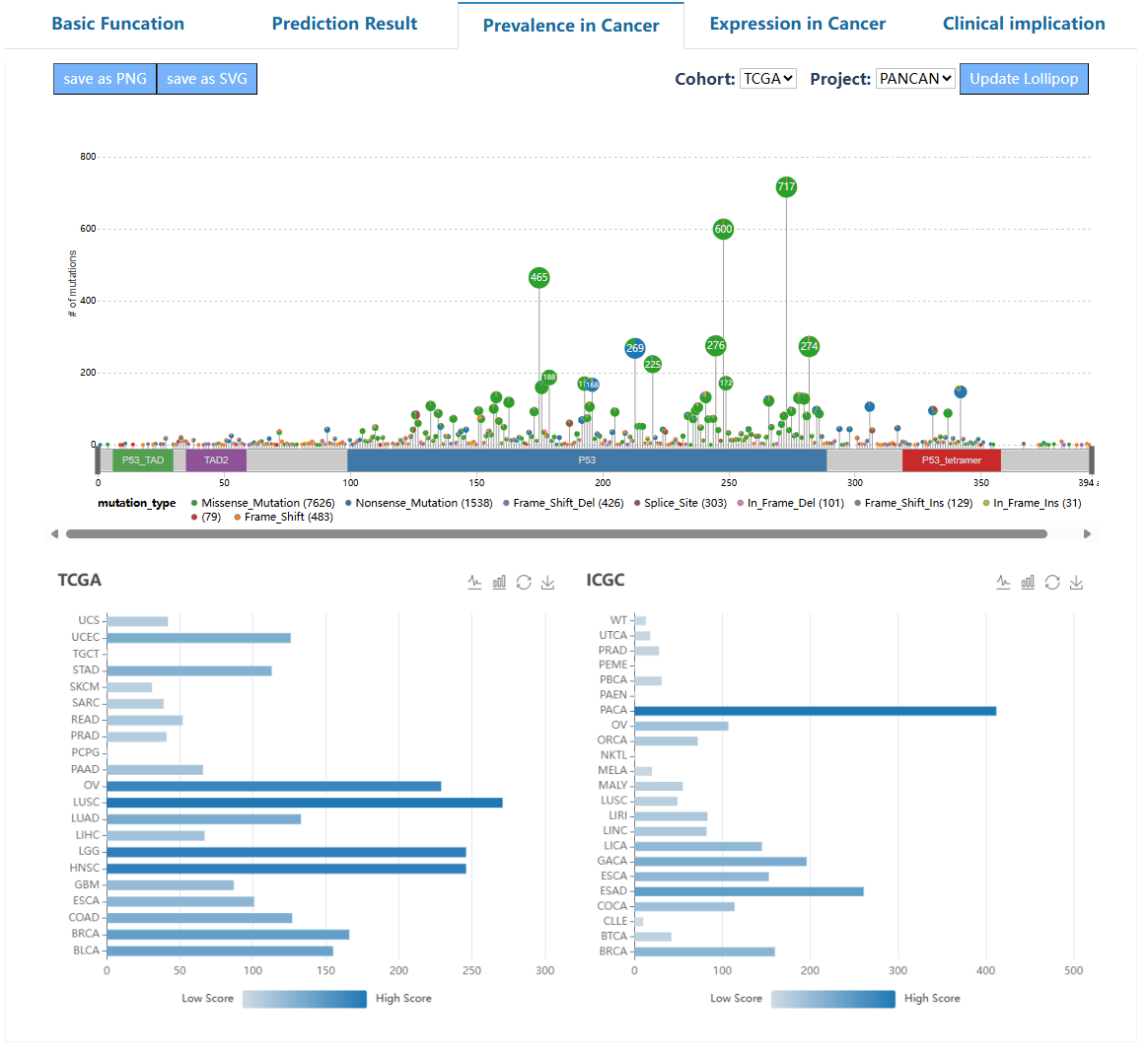
This page delineates the detailed information for driver mutations at the pan-cancer and tumor-type levels. For each driver mutation, we provide essential details on basic information, functional predictions, mutation prevalence in cancer, and potential clinical applications.
In the search page, users can input the interested mutation name to retrieve the driver mutation. Click on the "Reset" button to reset the search. Click on "Example 1", "Example 2" or "Example 3" to retrieve sample cases. The search results are linked to the detailed pages of related driver mutations. It's recommended to search for mutations in a specified format (e.g., 'PIK3CA_H1047R'). Alternatively, you can enter the gene (e.g., 'PIK3CA') to get a full list.
The full list of possible mutations associated with the queried gene, and allow clicking on a row in the table to get detailed information about mutation.

The basic information contains the 'Level' defined by OncoTriMD, 'Funcional annotation', and related links for the searched mutation. Users can search the external annotation information for the mutation by clicking on the corresponding hyperlink.



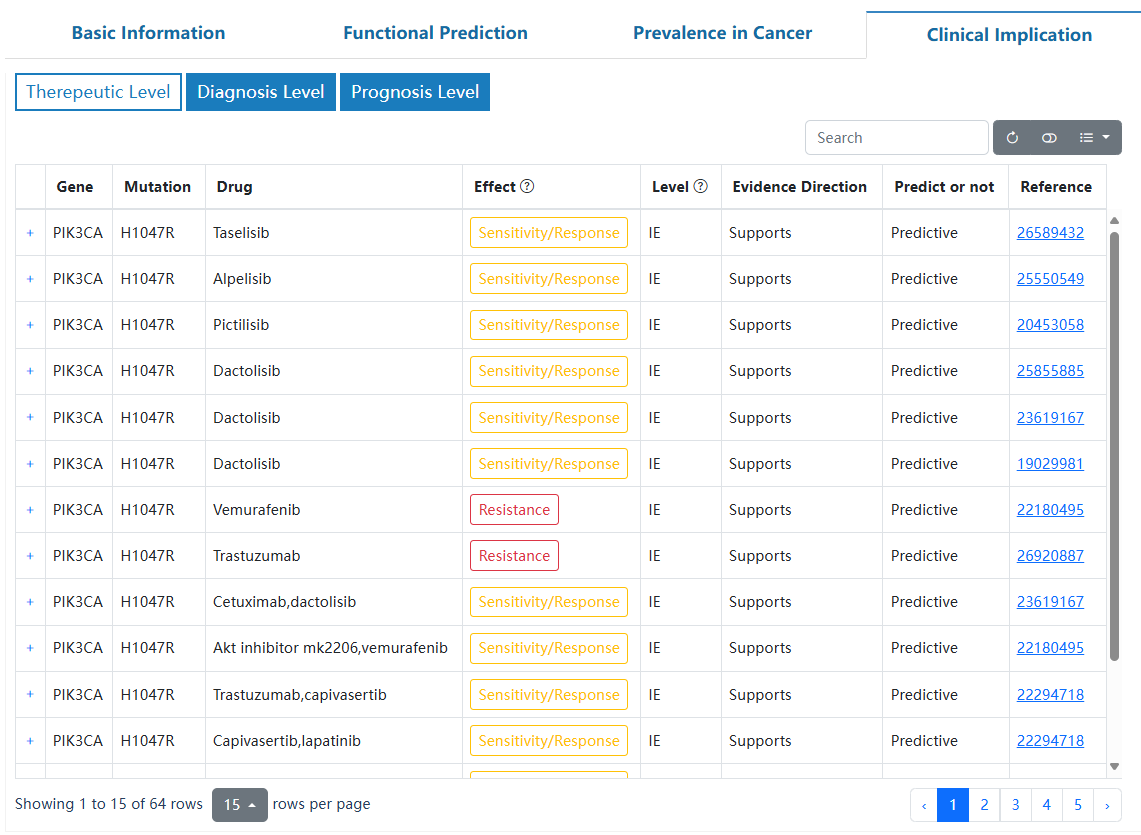
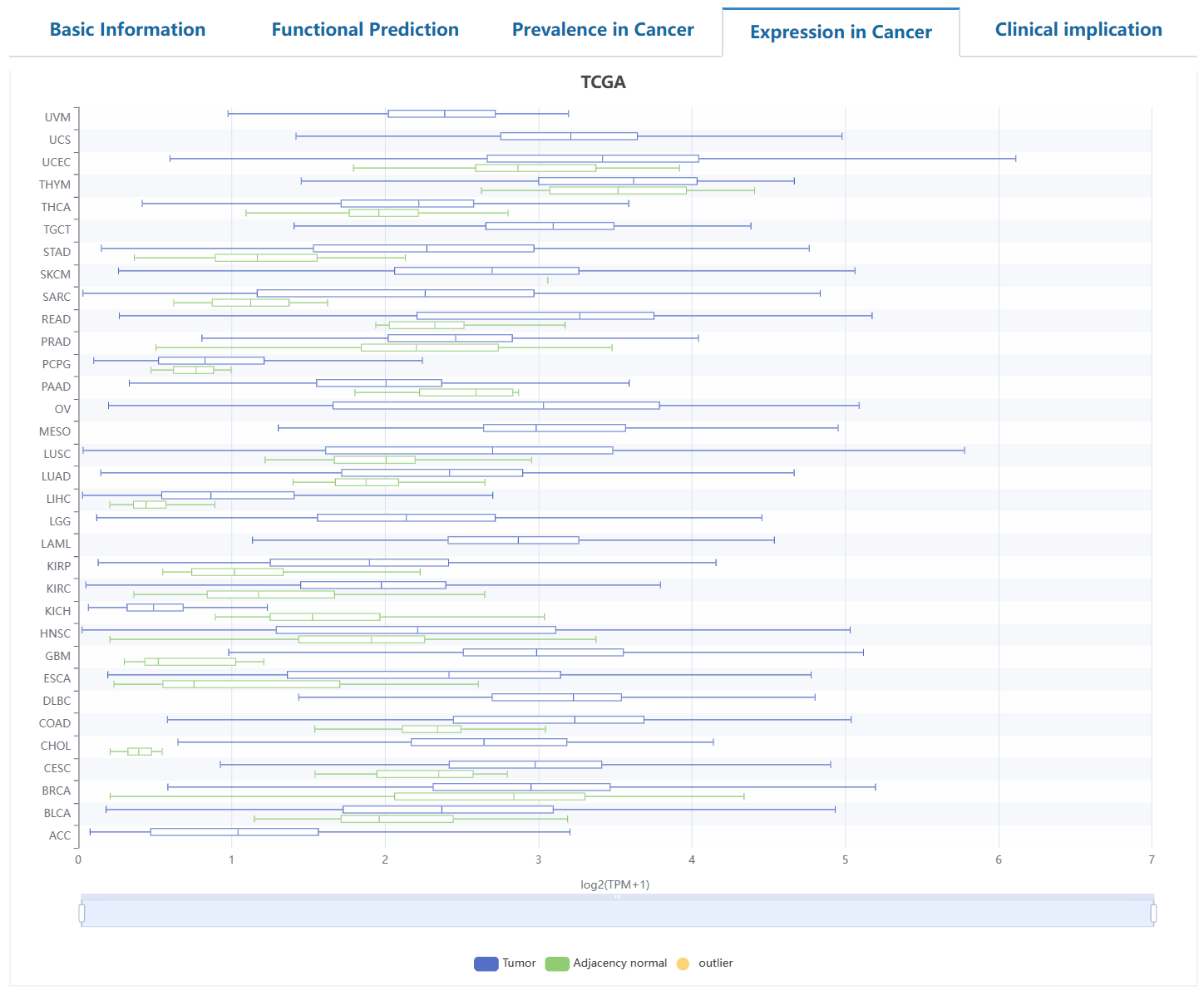
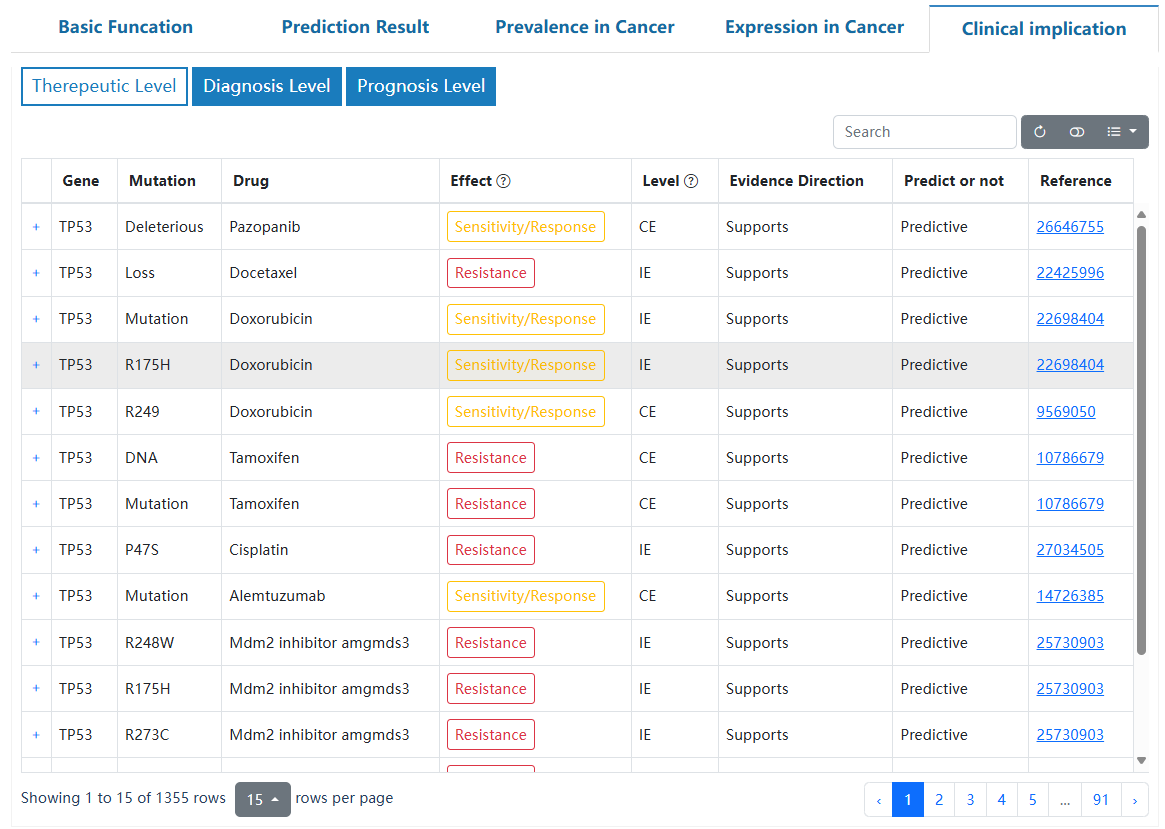
This page delineates the detailed information for driver genes at the pan-cancer and tumor-type levels. This page is structured to provide users with a comprehensive understanding of the annotated driver genes, such as the basic information, driving role in cancer, mutation prevalence, tumor differential expression, and potential clinical applications.
On the search page, users can input the interested gene name to retrieve the driver gene. Also, users can click the interested gene name in the gene-cloud graph for detailed information. Click on the "Reset" button to reset the search. Click on "Example" to retrieve sample cases.
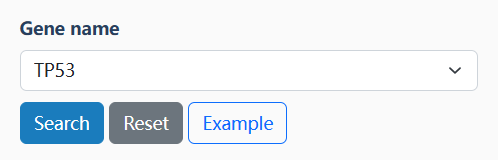

The basic information contains the 'Level' defined by OncoTriMD, 'Functional annotation', and related links for the searched gene. Users can search the external annotation information for the gene by clicking on the corresponding hyperlink.

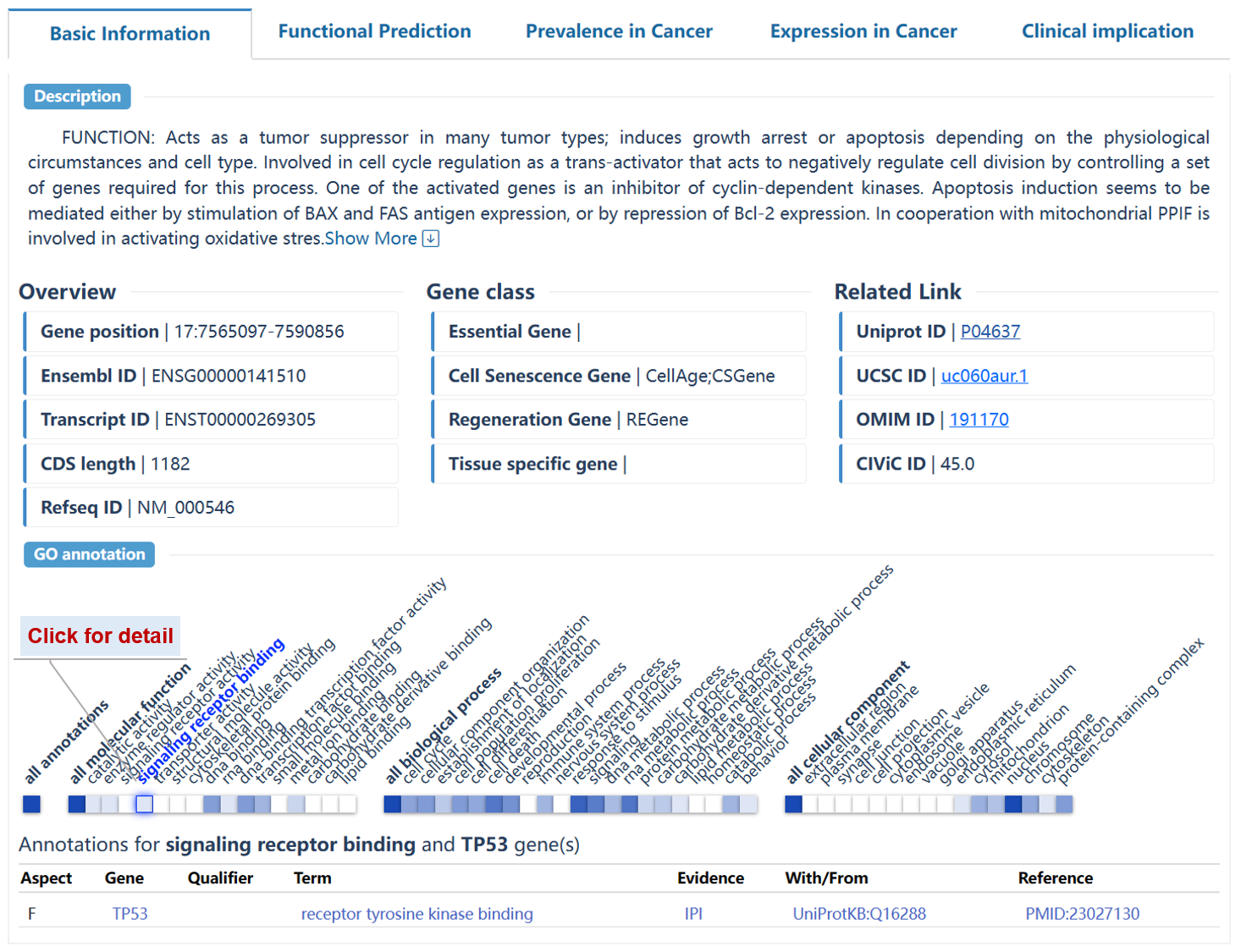
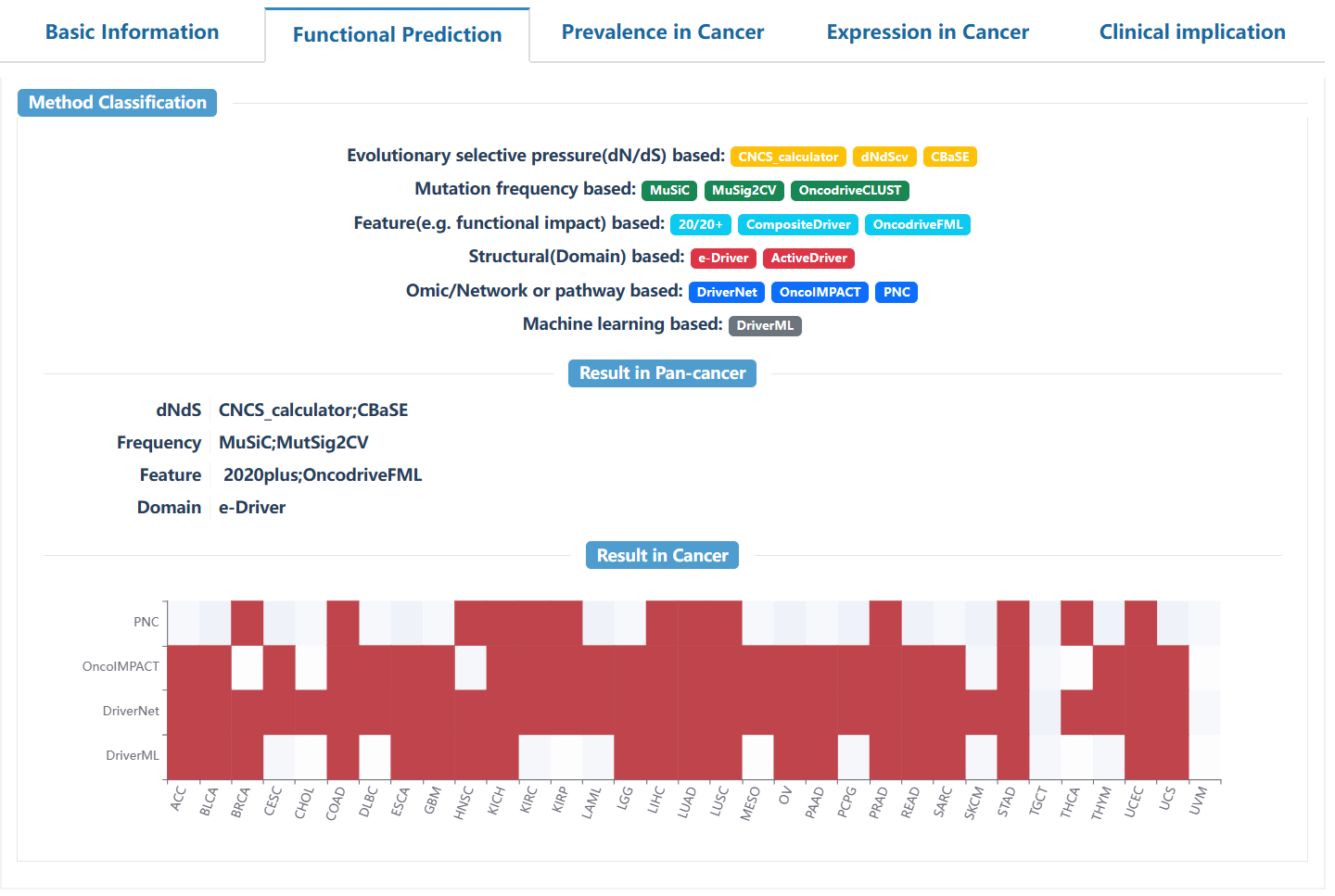
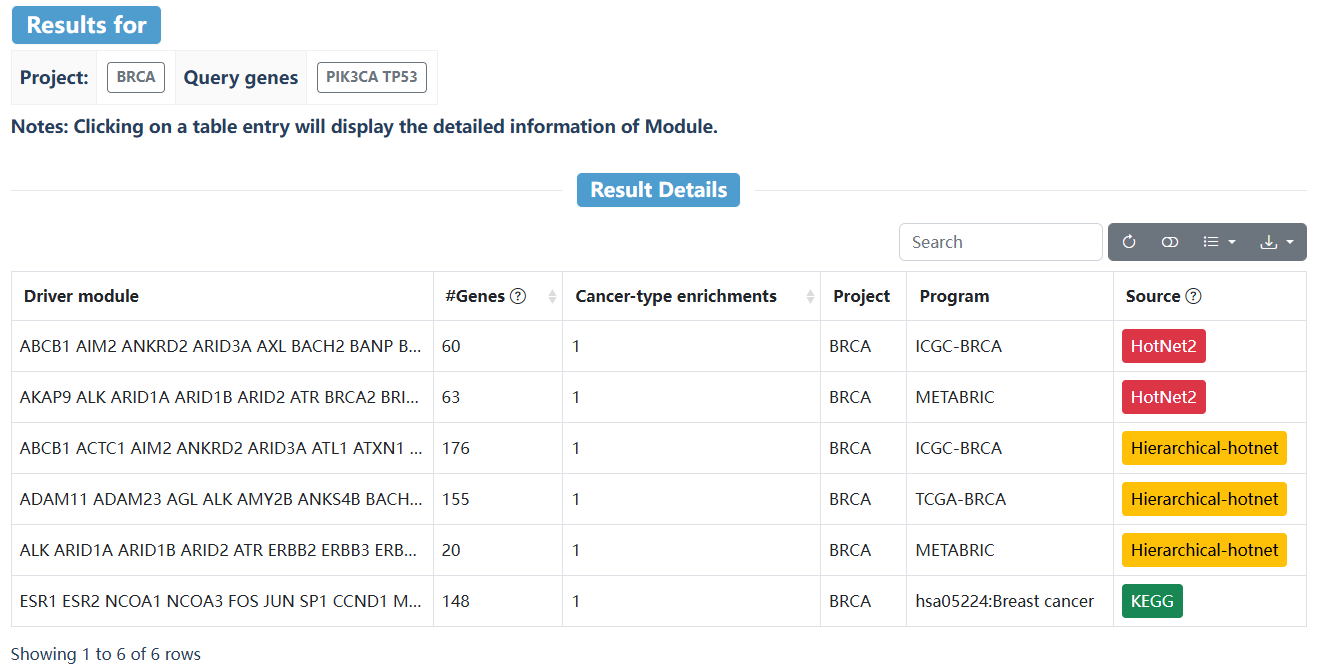
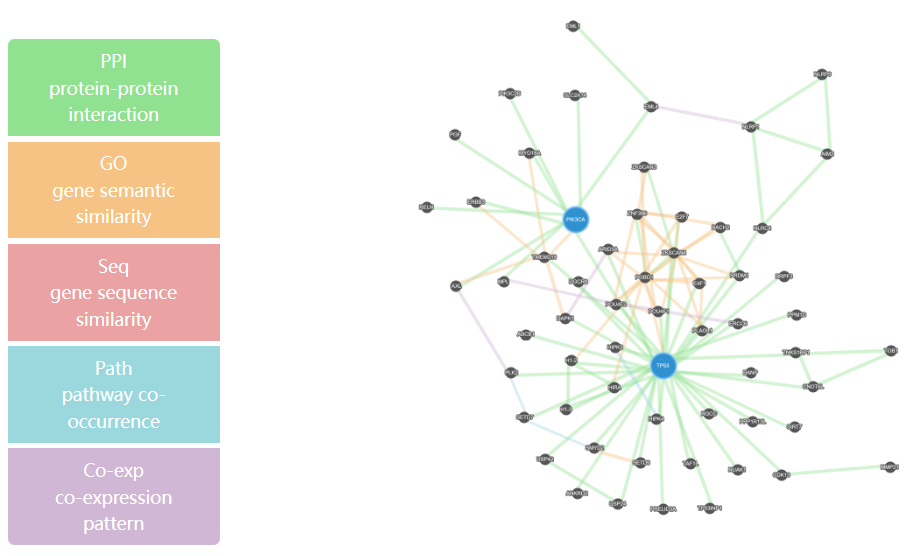
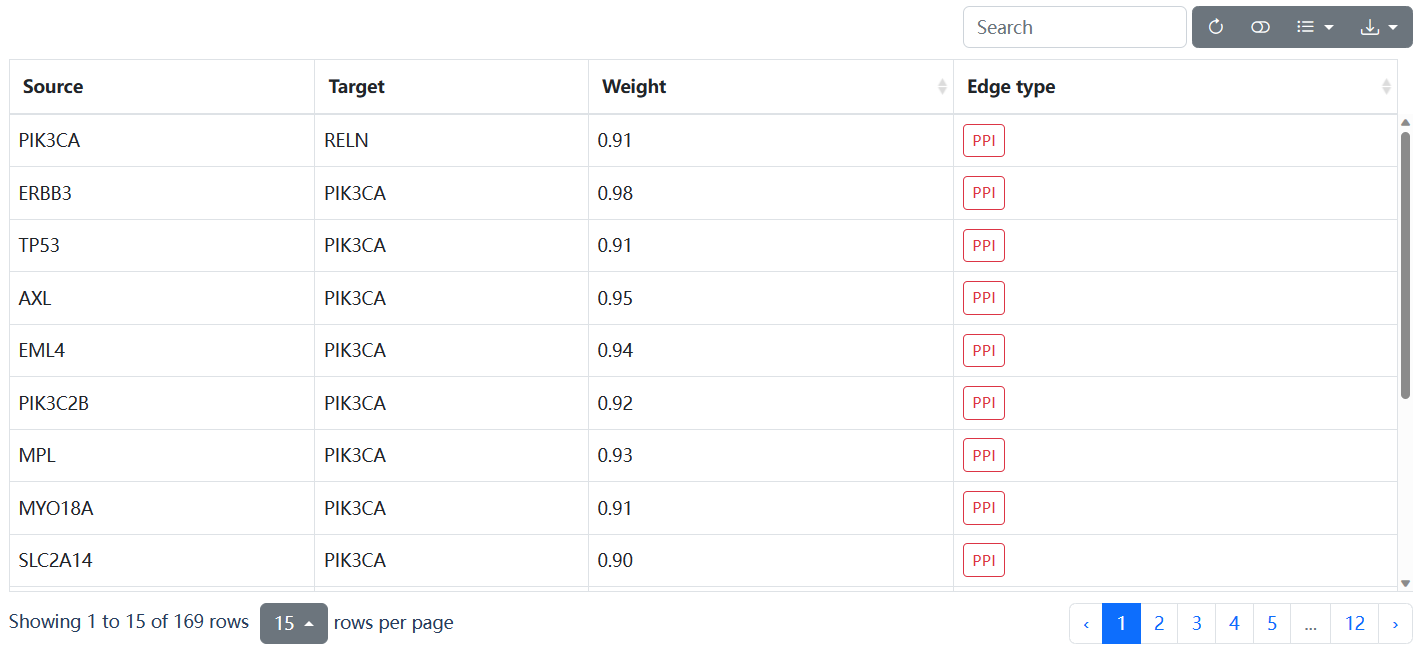
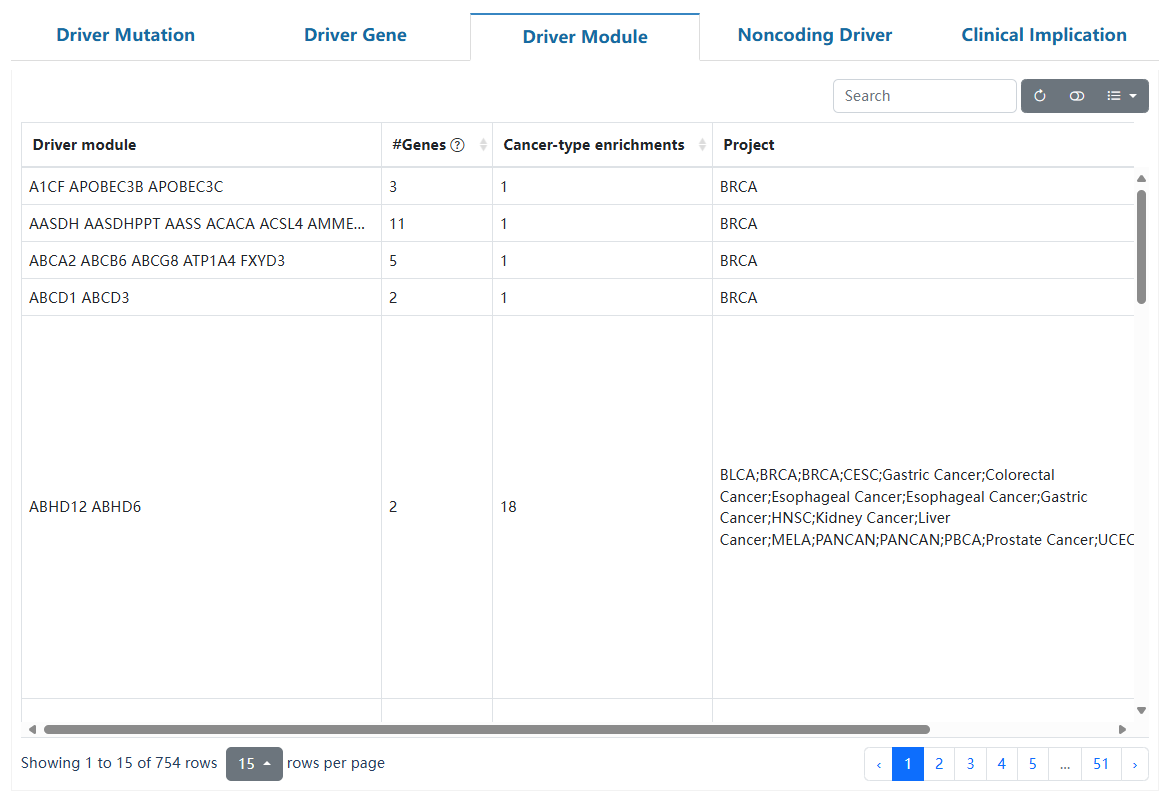
This page delineates the detailed information for driver modules predicted by HotNet2 or Hierarchical-hotnet, including the specific genes contained in the driver module, the GO function annotation, and the interaction network of genes in the module.
On the search page, users can select the interested method, program, and project from the drop-down box, and enter the gene name of interest to retrieve the driver module. Click on the "Reset" button to reset the search. Click on "Example 1" or "Example 2" to retrieve sample cases.
| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
| Driver module | Predicted driver module results by HotNet2, Hierarchical-hotnet, ActivatePathways, or pathway where the queried genes appear in the KEGG cancer pathway. |
| #Genes | The number of genes in the driver module. |
| Cancer-type enrichments | The module is predicted to be a driver module in different cancer types. |
| Project | The corresponding cancer types. |
| Program | The corresponding cancer cohort. |
| Source | HotNet2, Hierarchical-hotnet, ActivatePathways, or KEGG cancer pathway. |



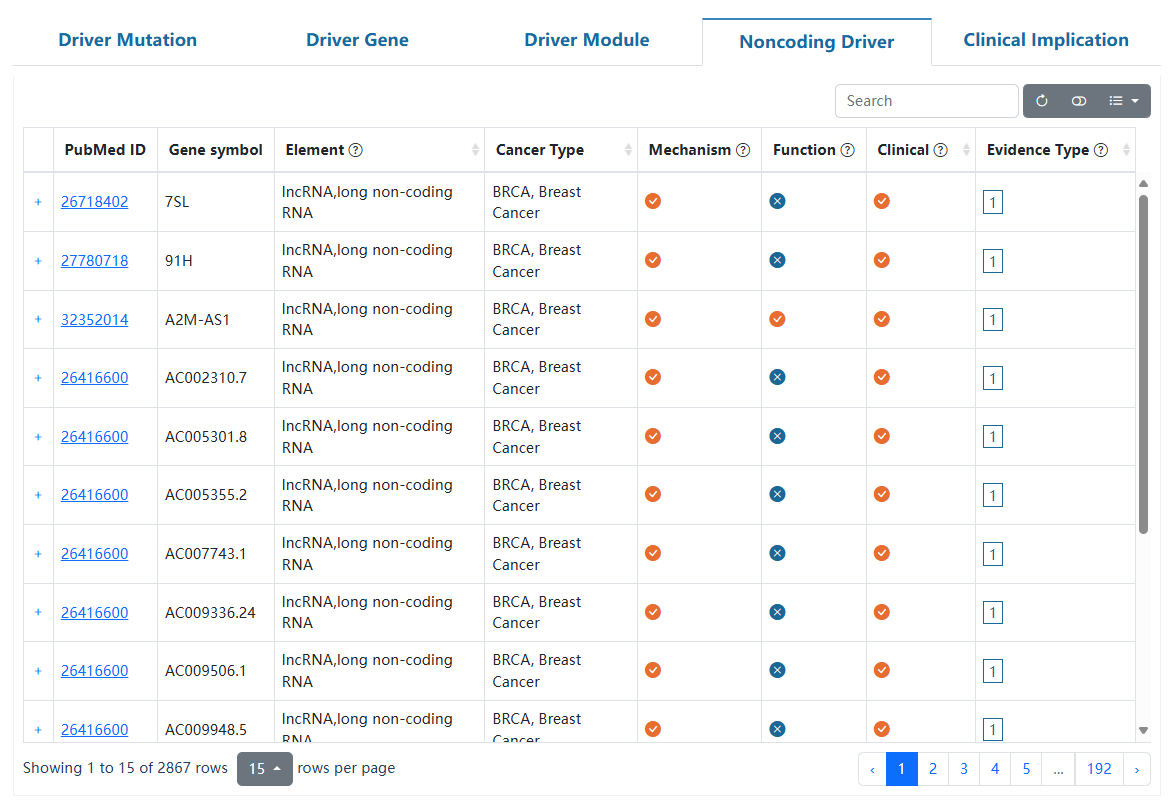
This page delineates the detailed information for non-coding drivers collected from several reputable databases and literature. For each non-coding driver, we collected its basic information, regulatory mechanisms, biological functions, and potential clinical applications from multiple sources.
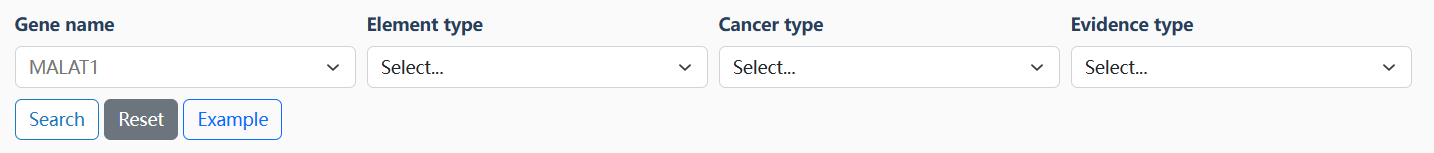
On the search page, users can input the interested gene name, element type, cancer type, and/or evidence type to retrieve the data. OncoTriMD supports the fuzzy search and will return all matching records. The search results are linked to the detailed pages of related non-coding drivers.
The basic information and related links for the queried gene or non-coding RNA. Users can search the external annotation information for the gene by clicking on the corresponding hyperlink.
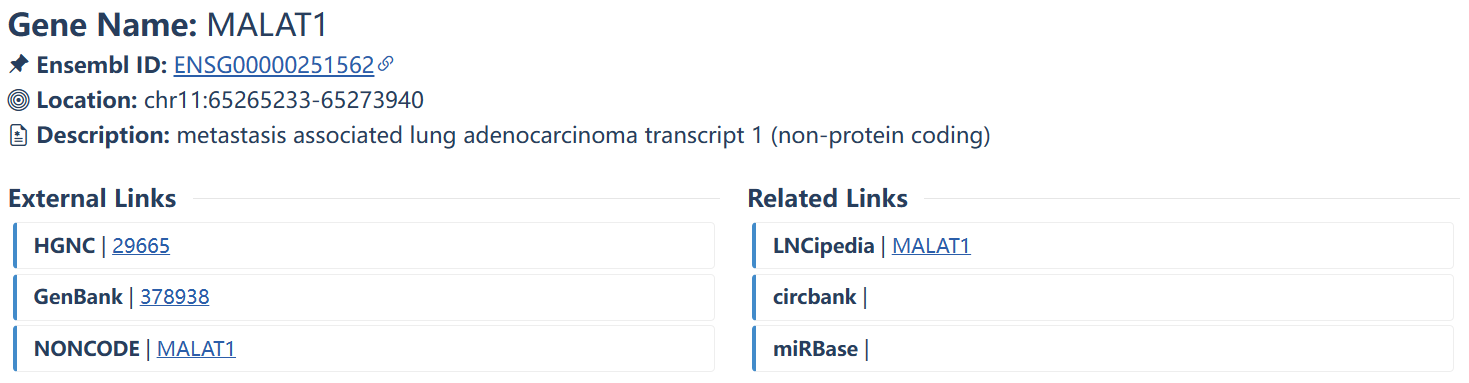
| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
| Click the '+' on the left to display a detailed annotation of the entry. | |
| Source | Data source for the entry. |
| PubMed ID | PubMed ID for the entry. Click to check the literature. |
| Gene symbol | Gene symbol for the entry. |
| Element | The element type of each entry encompasses various categories, including non-coding RNA (such as lncRNA, circRNA, miRNA), regulatory regions (such as enhancer, promoter, 3'UTR, 5'UTR) and pseudogenes. |
| Cancer Type | The related cancer type for the entry. |
| Mechanism/Function/Clinical | Indicates whether the entry contains information on mechanism, function and clinical. Click the '+' on the left to display a detailed annotation of the entry. |
| Evidence Type | The evidence type of the enrty. 1 represents experimentally validated evidence support, 2 represents differential gene expression association, and 3 represents results of computational prediction. Move the cursor over the evidence type and the method used to obtain the evidence will be hovered. |
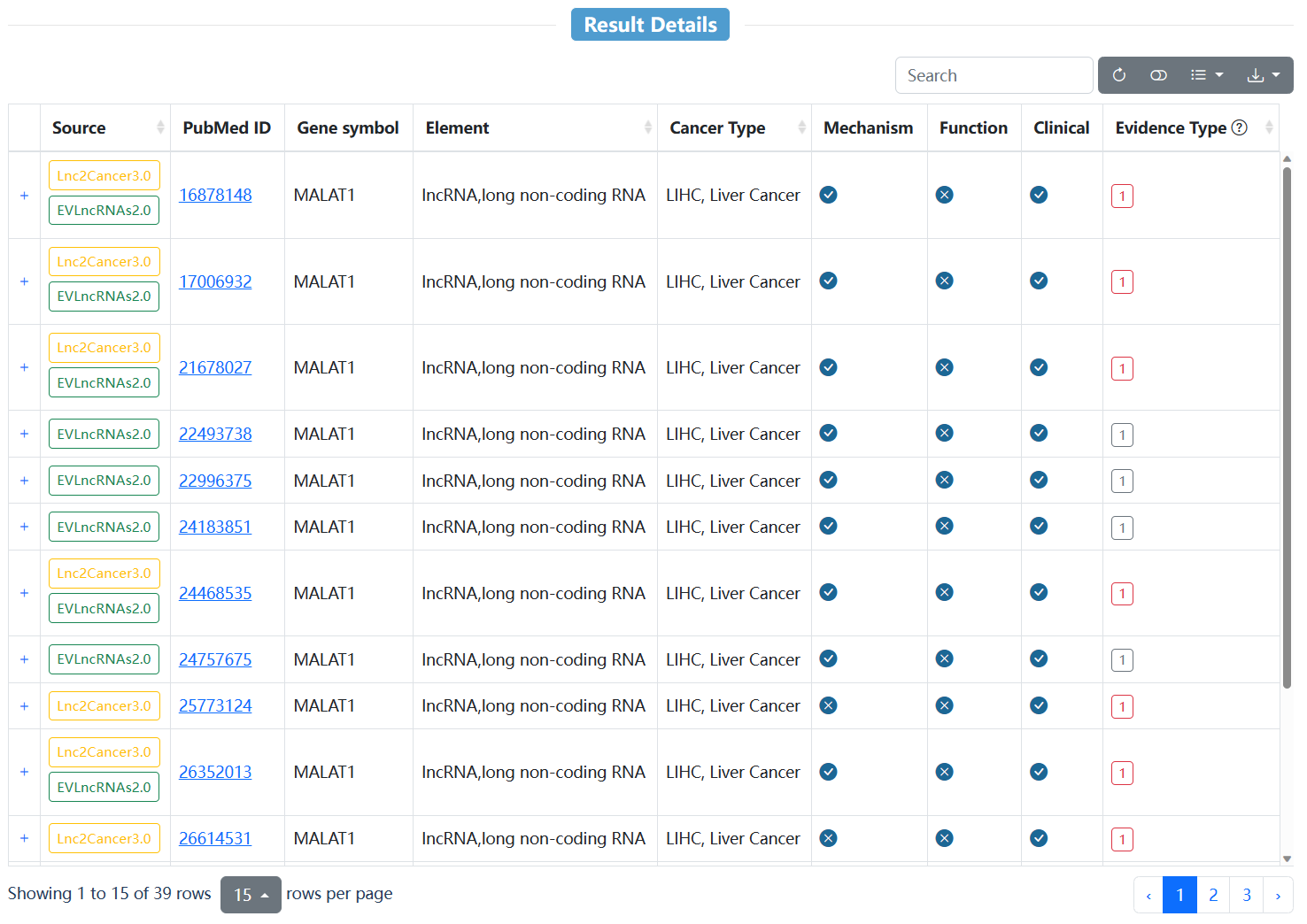
This table shows a detailed annotation of the entry. Regulatory mechanisms document the type of regulation to which the element is subjected within the context of cancer, including transcription factor (TF), enhancer, variant, microRNA (miRNA), epigenetic modification, and alteration in gene expression. Biological functions document how the element contributes to cancer development and progression, such as cell growth, apoptosis/autophagy, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), immunity escape, alterations in coding ability and inflammation. Clinical applications document the potential use of the element as a biomarker for cancer, including its ability to predict clinical events such as metastasis, recurrence, circulation, drug/therapy/stress-resistance, and prognosis.

This page systematically organizes driver mutations, driver genes, driver modules, and non-coding drivers in different cancer types. Users can access the cancer-specific driver list exclusively provided by OncoTriMD based on the mutation cohort and cancer type of interest.
On the search page, users can select interested programs and cancer types from the drop-down box to search for drivers specific to that cancer type. Click on the "Reset" button to reset the search. Click on "Example" to retrieve sample cases.

| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
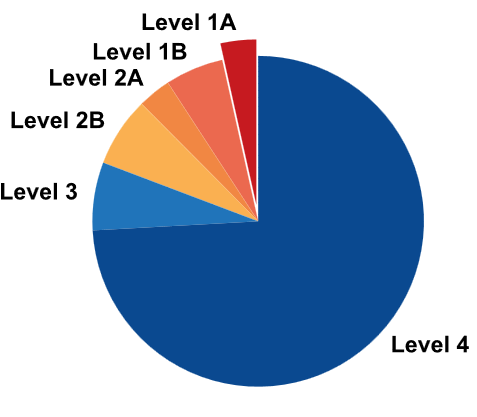
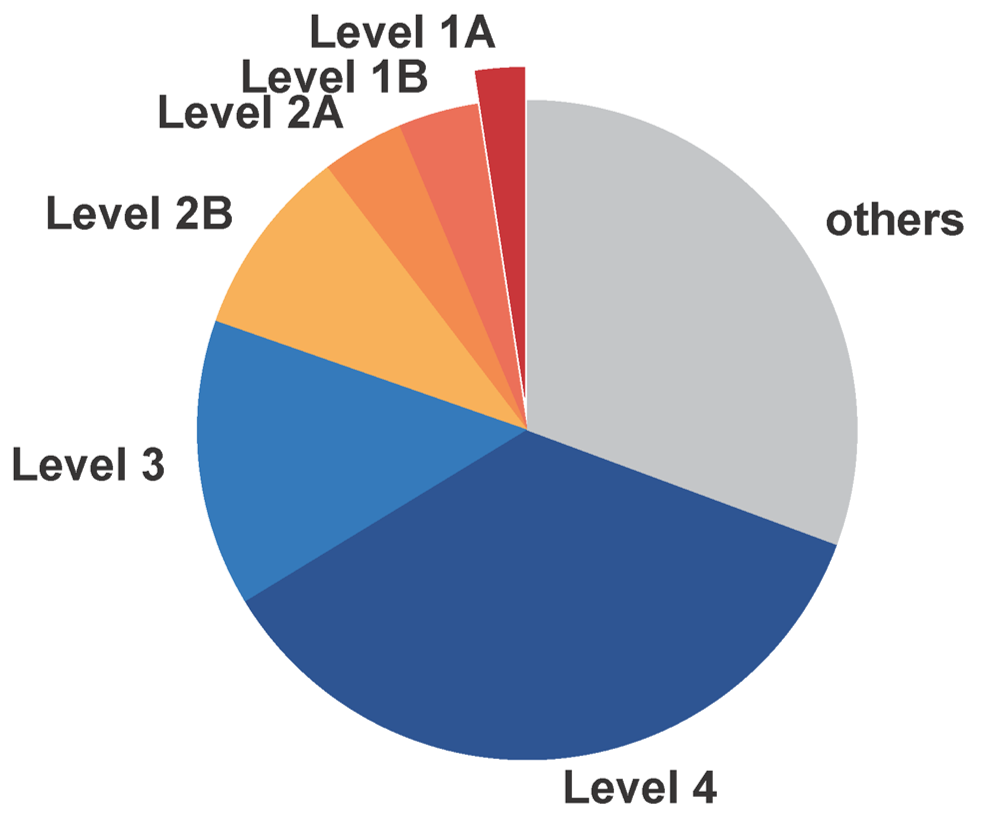
| Level | The level of mutations is determined according to our accumulated evidence and customized criteria. For detailed ranking criteria, please consult the framework diagram provided in the database. |
| Gene symbol | Gene symbol for the entry. |
| Gene ID | The Ensembl gene ID of the gene. |
| ENST | The Ensembl transcript ID of the gene. |
| Mutation | The specific mutation of the protein by indicating the original amino acid, its position in the protein sequence, and the mutated amino acid. |
| Frequency | The number of somatic mutations observed at this cancer type. |
| Q(z) | The posterior probability of this amino acid site being a cancer driver. |
| M(z) | The posterior mean of recurrent mutations of this amino acid site. |
| OncoVar | Whether or not annotated by OncoVar |
| OncoKB | Whether or not annotated by OncoKB. |

| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
| Level | The level of genes is determined according to our accumulated evidence and customized criteria. For detailed ranking criteria, please consult the framework diagram provided in the database. |
| Gene symbol | Gene symbol for the entry. |
| Gene type | Gene type identified by Two-Component CN/CS. |
| Gene ID | The Ensembl gene ID of the gene. |
| #Nonsynonymous | The number of nonsynonymous mutations counted in the protein-coding region of the gene. |
| #Synonymous | The number of synonymous mutations counted in the protein-coding region of the gene. |
| CN/CS | The CN/CS ratio of a gene is defined by the ratio of the nonsynonymous mutation rate to the synonymous mutation rate in cancer samples. |
| P value | The χ2 test was conducted for the gene to test the statistical significance of the difference between the CN/CS values and 1. |
| OncoVar | Whether or not annotated by OncoVar |
| OncoKB | Whether or not annotated by OncoKB. |

| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
| Driver module | The driver module results. |
| #Genes | The number of genes in the driver module. |
| Cancer-type enrichments | The module is predicted to be a driver module in different cancer types. |
| Project | The corresponding cancer types. |
| Program | The corresponding cancer cohort(TCGA/ICGC). |
| Column head | Description |
|---|---|
| Click the '+' on the left to display a detailed annotation of the entry. | |
| Source | Data source for the entry. |
| PubMed ID | PubMed ID for the entry. Click to check the literature. |
| Gene symbol | Gene symbol for the entry. |
| Element | The element type of each entry encompasses various categories, including non-coding RNA (such as lncRNA, circRNA, miRNA), regulatory regions (such as enhancer, promoter, 3'UTR, 5'UTR) and pseudogenes. |
| Cancer Type | The related cancer type for the entry. |
| Mechanism/Function/Clinical | Indicates whether the entry contains information on mechanism, function and clinical. Click the '+' on the left to display a detailed annotation of the entry. |
| Evidence Type | The evidence type of the enrty. 1 represents experimentally validated evidence support, 2 represents differential gene expression association, and 3 represents results of computational prediction. Move the cursor over the evidence type and the method used to obtain the evidence will be hovered. |
This page provides web tools of three in-house cancer driver prediction tools to help users freely explore cancer drivers in their mutation data through a standardized workflow.

This database is hosted by Pharmacogenomics Group, College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University