Spatial-pseudotime anatomy and transcriptome reveal two types of meristematic pools within secondary vascular tissue of poplar woody stem
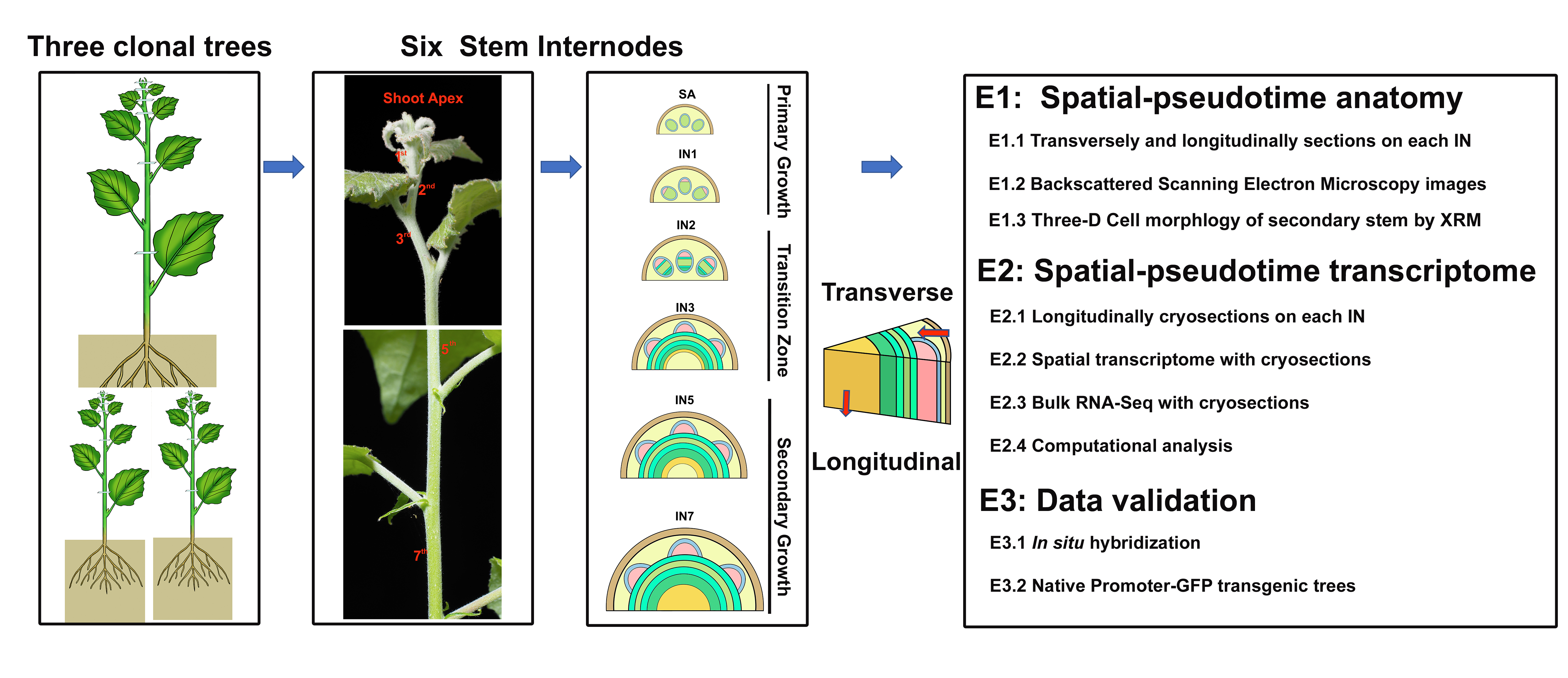
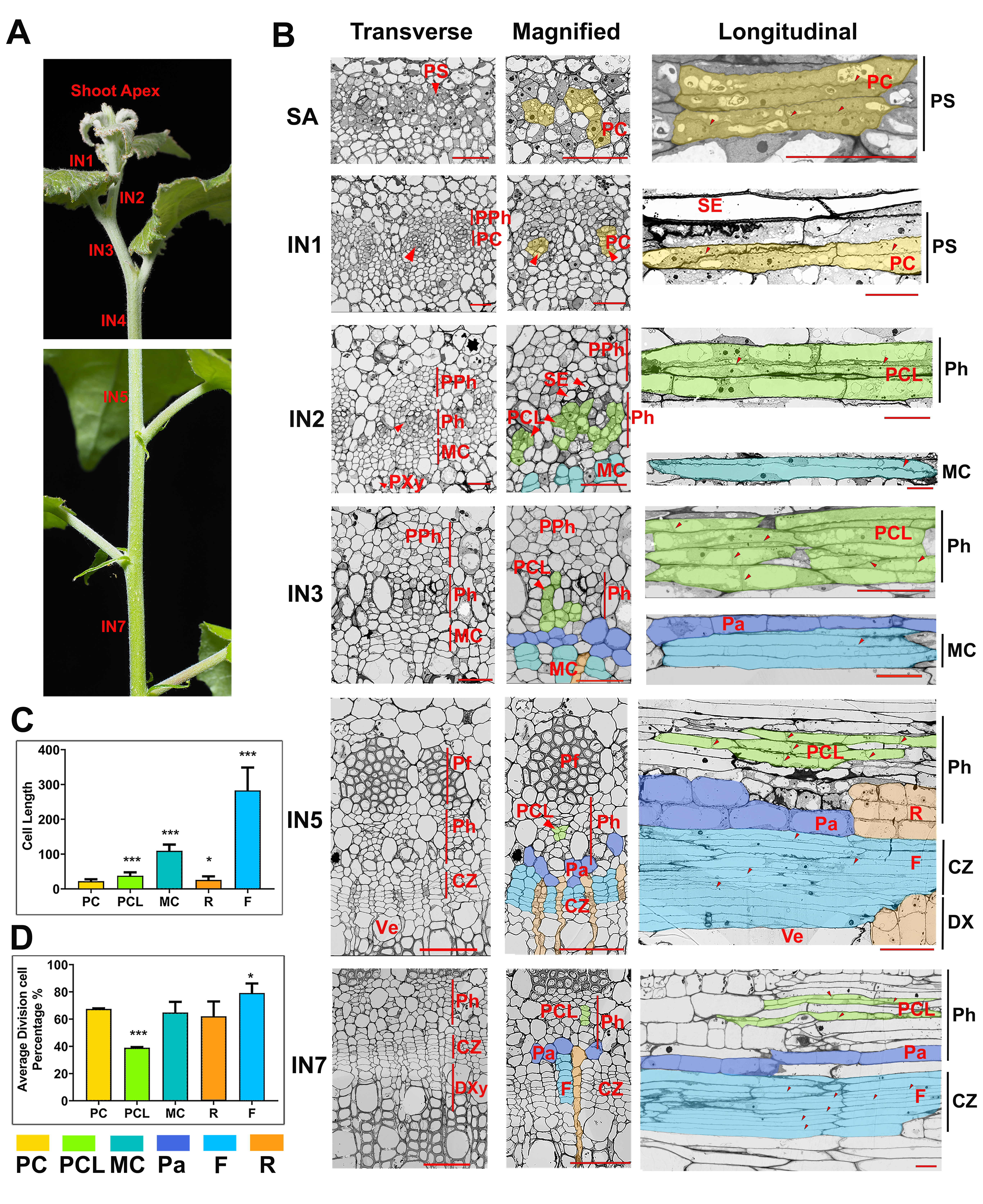
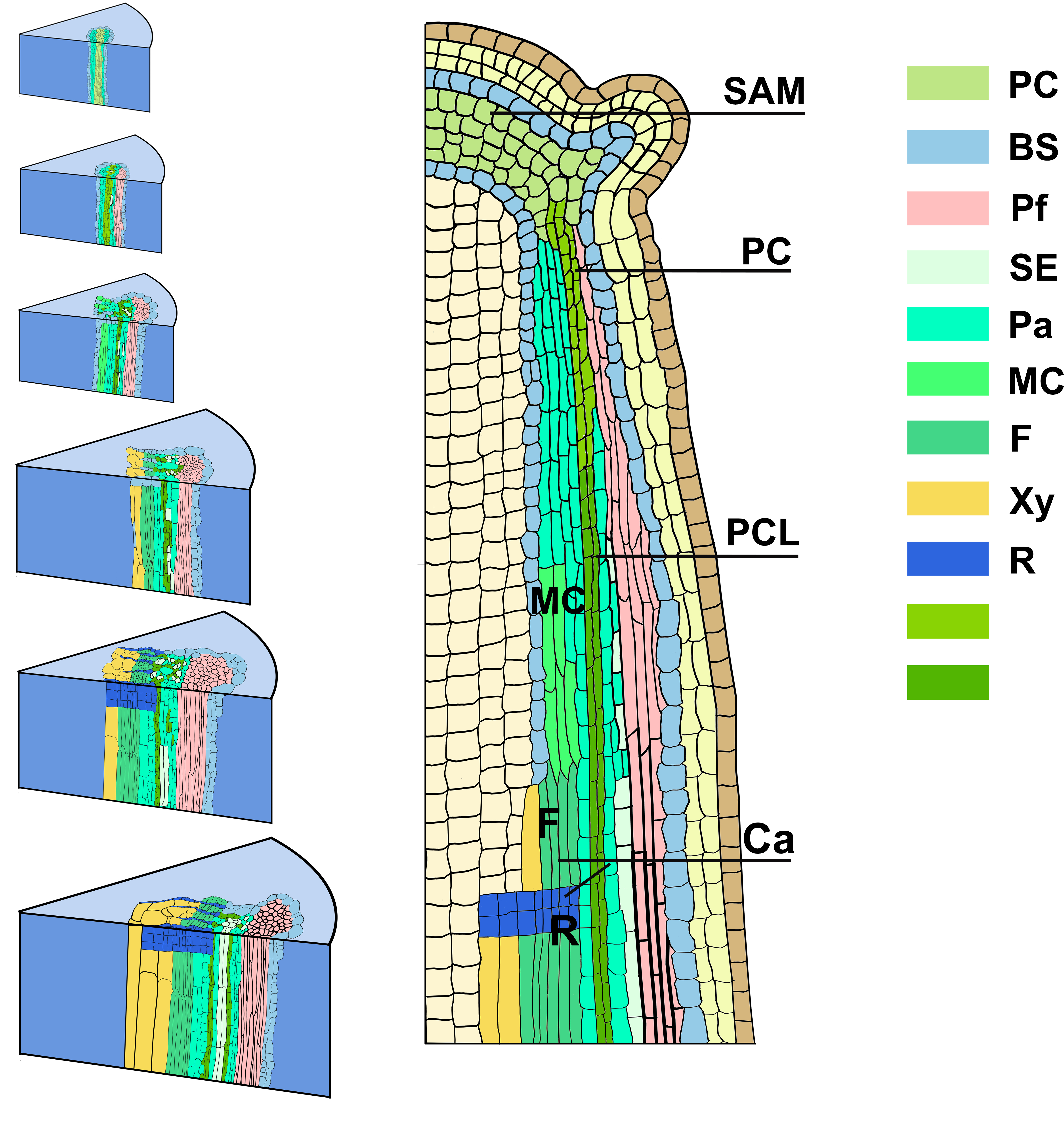
In this stusy, we combined high-resolution anatomical analysis with a spatial transcriptome (ST) technique to define features of meristematic cells in a developmental gradient from primary to secondary vascular tissues in poplar stems. The tissue-specific gene expression of meristems and derived vascular tissue types were accordingly mapped to specific anatomical domains. The resulting gene expression atlas and the transcriptional network spanning the primary transition to secondary vascular tissues provide a novel resource to guide research and new applications for the regulation of meristems activities and the evolution of vascular plants.
| Potri ID | Ath ID | Protein Info | Expression level(mean) |
|---|
Contact us
Dr. Juan Du, State Key Laboratory of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China djuan@zju.edu.cn
Wenfan Chen, Institute of Quantitative Biology, College of Life Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China wenfanchen@zju.edu.cn
How to cite
Du et al., High-resolution anatomical and spatial transcriptome analyses reveal two types of meristematic cell pools within the secondary vascular tissue of poplar stem, Molecular Plant (2023), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2023.03.005
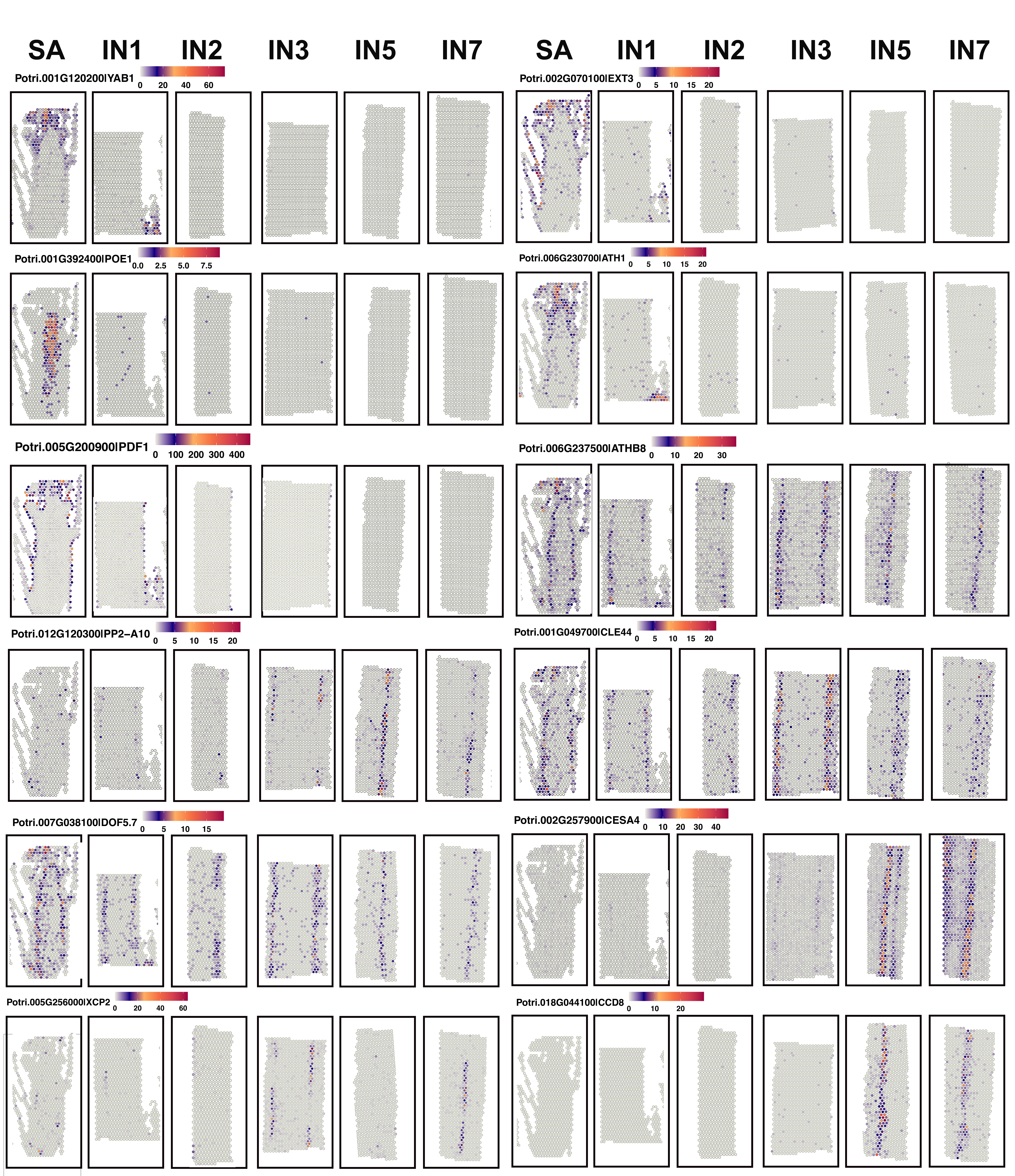
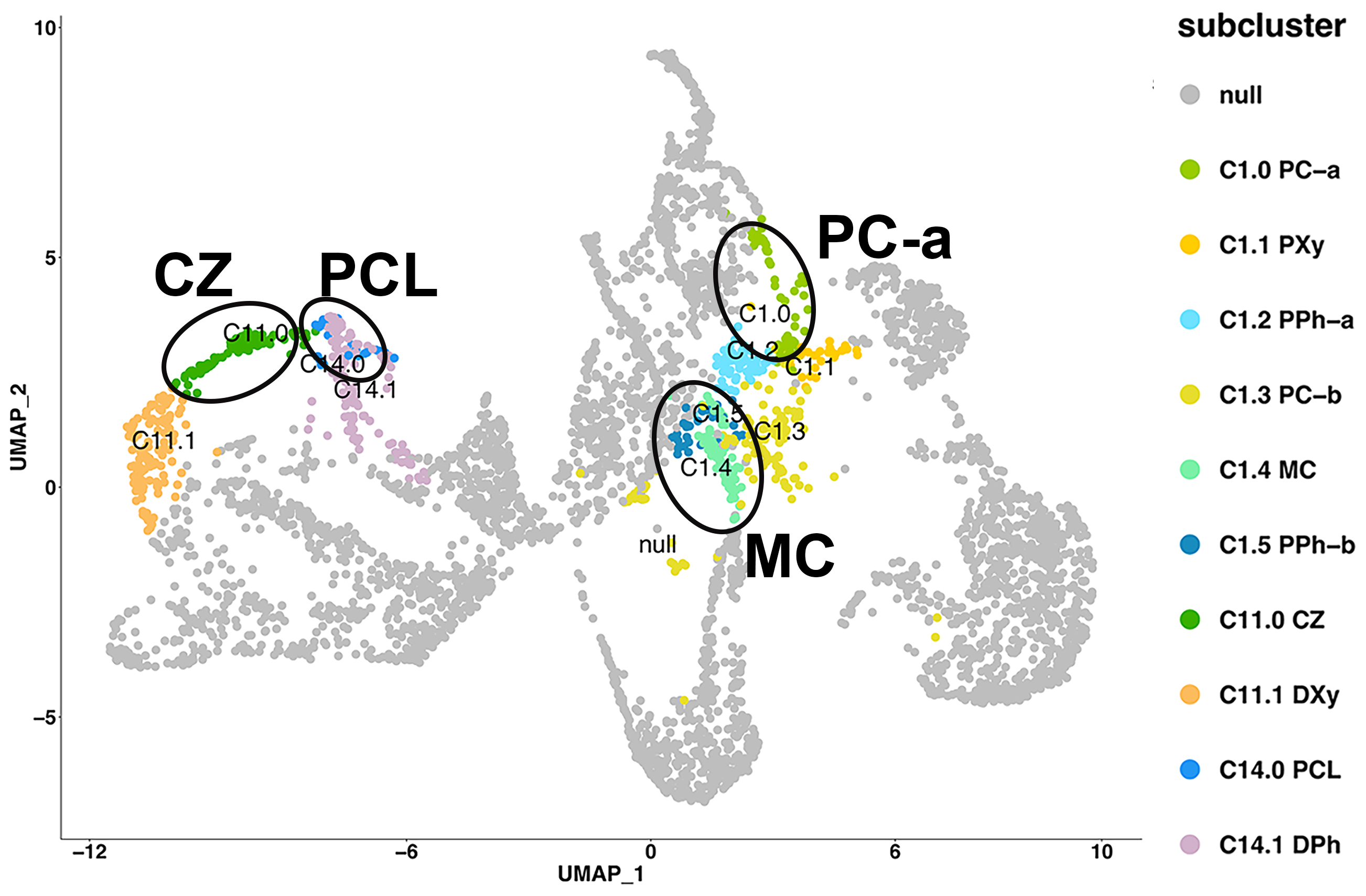
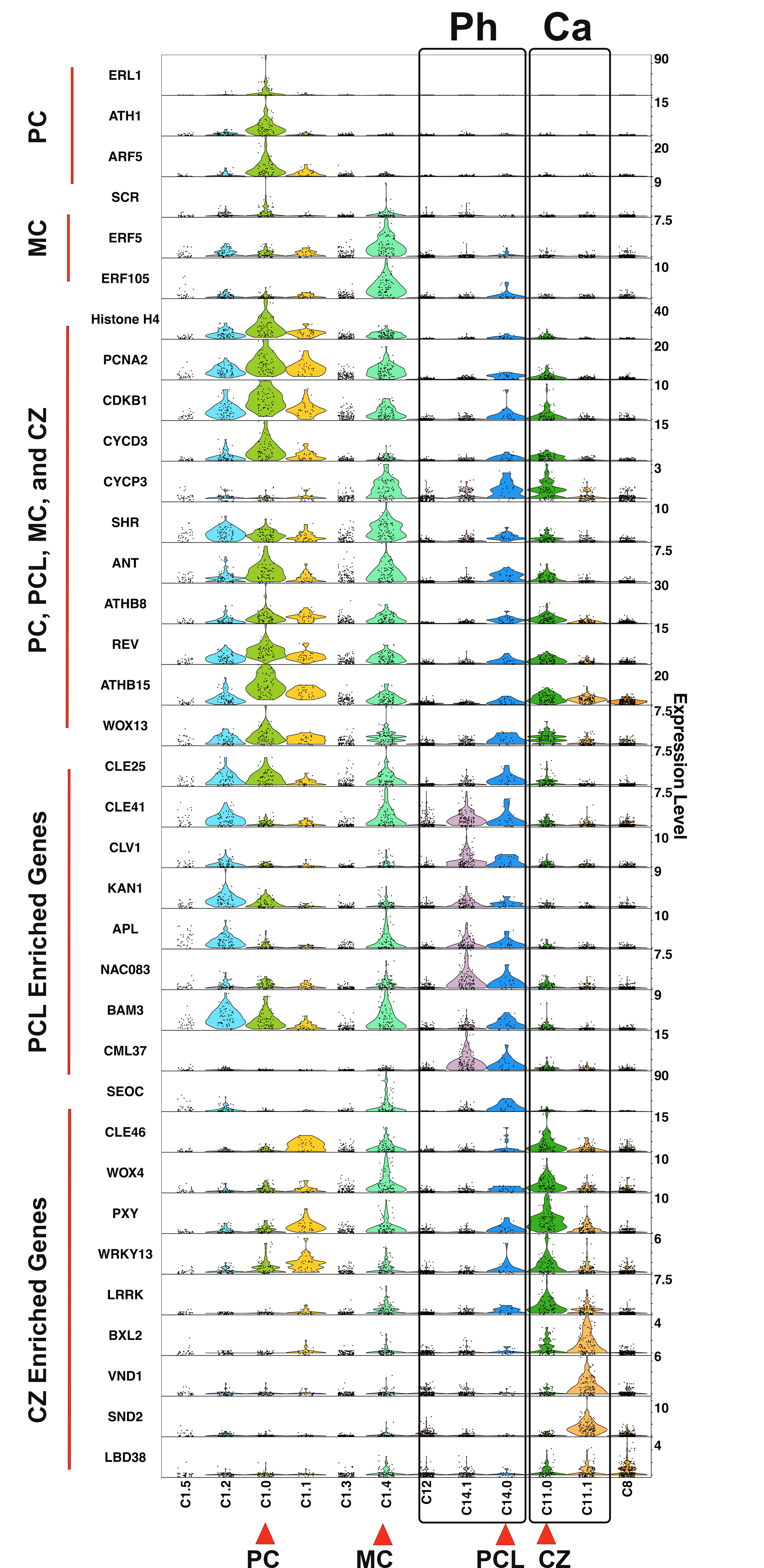
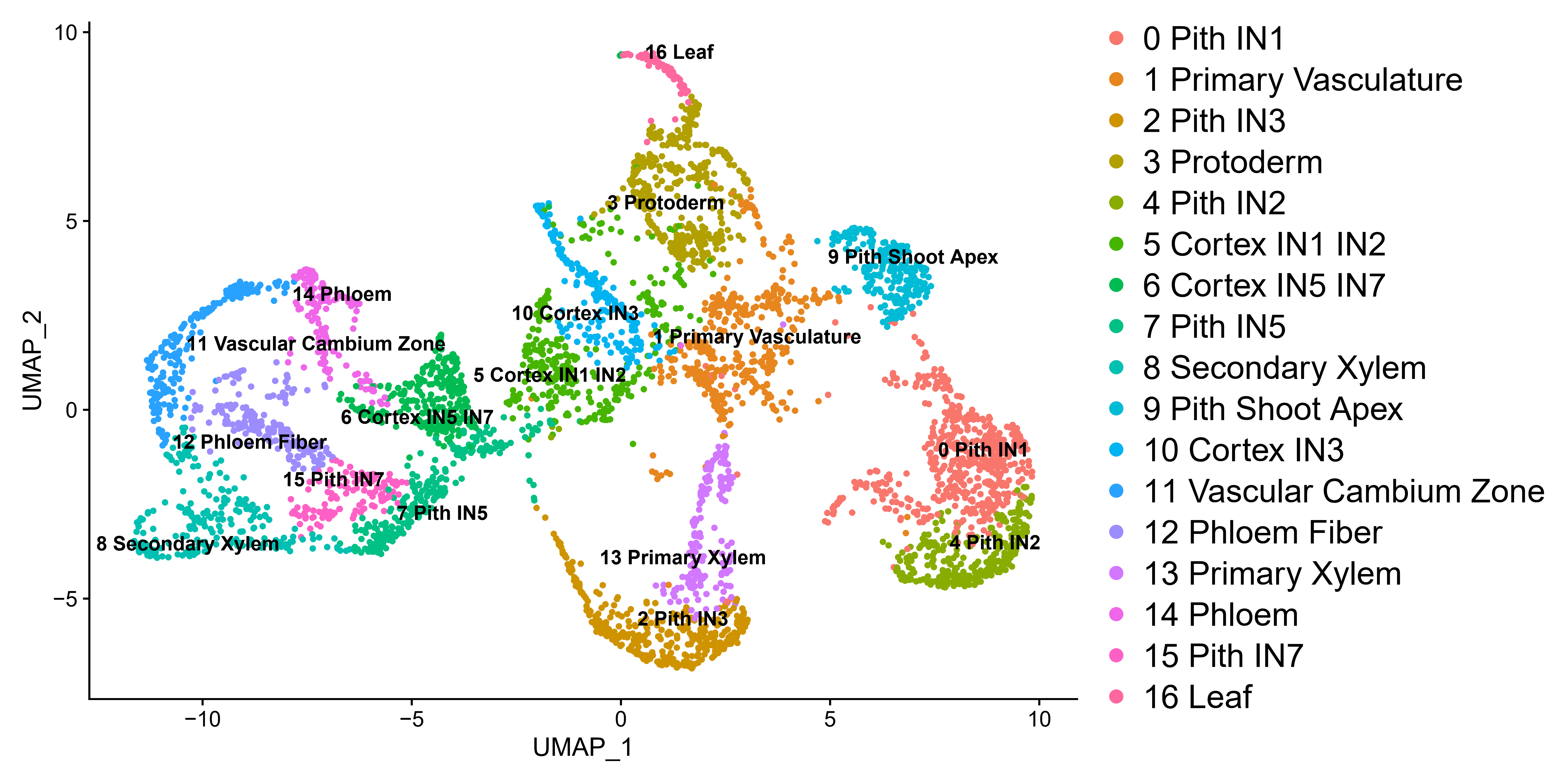
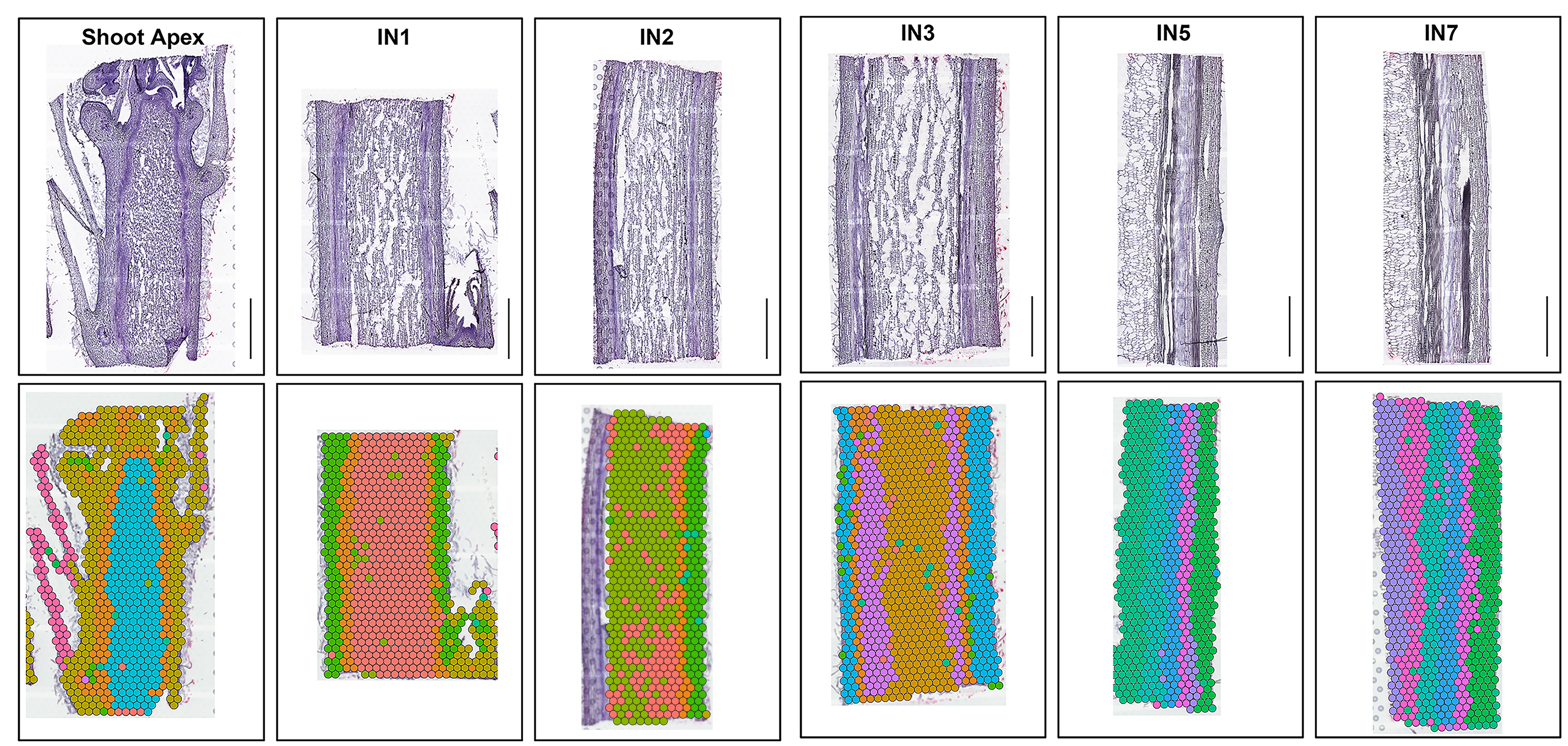
Spatial distribution of cluster marker genes